03/24/18
Filed under:
General
Posted by:
site admin @ 7:08 pm
2571 Sun 25 Mar 2018 LESSON Article is about human language in general
Language
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A mural in Teotihuacan, Mexico (c. 2nd century) depicting a person emitting a speech scroll from his mouth, symbolizing speech
Language is a system that consists of the development, acquisition, maintenance and use of complex systems of communication, particularly the human ability to do so; and a language is any specific example of such a system.
The scientific study of language is called linguistics. Questions concerning the philosophy of language, such as whether words can represent experience, have been debated at least since Gorgias and Plato in ancient Greece. Thinkers such as Rousseau have argued that language originated from emotions while others like Kant have held that it originated from rational and logical thought. 20th-century philosophers such as Wittgenstein argued that philosophy is really the study of language. Major figures in linguistics include Ferdinand de Saussure and Noam Chomsky.
Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between
5,000 and 7,000. However, any precise estimate depends on a partly
arbitrary distinction between languages and dialects. Natural languages are spoken or signed, but any language can be encoded into secondary media using auditory, visual, or tactile stimuli – for example, in whistling, signed, or braille. This is because human language is modality-independent. Depending on philosophical perspectives regarding the definition of language and meaning, when used as a general concept, “language” may refer to the cognitive
ability to learn and use systems of complex communication, or to
describe the set of rules that makes up these systems, or the set of
utterances that can be produced from those rules. All languages rely on
the process of semiosis to relate signs to particular meanings. Oral, manual and tactile languages contain a phonological system that governs how symbols are used to form sequences known as words or morphemes, and a syntactic system that governs how words and morphemes are combined to form phrases and utterances.
Human language has the properties of productivity and displacement,
and relies entirely on social convention and learning. Its complex
structure affords a much wider range of expressions than any known
system of animal communication. Language is thought to have originated when early hominins started gradually changing their primate communication systems, acquiring the ability to form a theory of other minds and a shared intentionality.[1][2]
This development is sometimes thought to have coincided with an
increase in brain volume, and many linguists see the structures of
language as having evolved to serve specific communicative and social
functions. Language is processed in many different locations in the human brain, but especially in Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas. Humans acquire
language through social interaction in early childhood, and children
generally speak fluently by approximately three years old. The use of
language is deeply entrenched in human culture.
Therefore, in addition to its strictly communicative uses, language
also has many social and cultural uses, such as signifying group identity, social stratification, as well as social grooming and entertainment.
Languages evolve and diversify over time, and the history of their evolution can be reconstructed by comparing
modern languages to determine which traits their ancestral languages
must have had in order for the later developmental stages to occur. A
group of languages that descend from a common ancestor is known as a language family. The Indo-European family is the most widely spoken and includes languages as diverse as English, Russian and Hindi; the Sino-Tibetan family, which includes Mandarin, Bodo and the other Chinese languages, and Tibetan; the Afro-Asiatic family, which includes Arabic, Somali, and Hebrew; the Bantu languages, which include Swahili, and Zulu, and hundreds of other languages spoken throughout Africa; and the Malayo-Polynesian languages, which include Indonesian, Malay, Tagalog, and hundreds of other languages spoken throughout the Pacific. The languages of the Dravidian family that are spoken mostly in Southern India include Tamil and Telugu.
Academic consensus holds that between 50% and 90% of languages spoken
at the beginning of the 21st century will probably have become extinct by the year 2100.
Definitions
The English word language derives ultimately from Proto-Indo-European *dn̥ǵʰwéh₂s “tongue, speech, language” through Latin lingua, “language; tongue”, and Old French language.[3] The word is sometimes used to refer to codes, ciphers, and other kinds of artificially constructed communication systems such as formally defined computer languages used for computer programming. Unlike conventional human languages, a formal language in this sense is a system of signs for encoding and decoding information. This article specifically concerns the properties of natural human language as it is studied in the discipline of linguistics.
As an object of linguistic study, “language” has two primary
meanings: an abstract concept, and a specific linguistic system, e.g. “French“. The Swiss linguist Ferdinand de Saussure, who defined the modern discipline of linguistics, first explicitly formulated the distinction using the French word langage for language as a concept, langue as a specific instance of a language system, and parole for the concrete usage of speech in a particular language.[4]
When speaking of language as a general concept, definitions can be used which stress different aspects of the phenomenon.[5]
These definitions also entail different approaches and understandings
of language, and they also inform different and often incompatible
schools of linguistic theory.[6] Debates about the nature and origin of language go back to the ancient world. Greek philosophers such as Gorgias and Plato
debated the relation between words, concepts and reality. Gorgias
argued that language could represent neither the objective experience
nor human experience, and that communication and truth were therefore
impossible. Plato maintained that communication is possible because
language represents ideas and concepts that exist independently of, and
prior to, language.
During the Enlightenment and its debates about human origins, it became fashionable to speculate about the origin of language. Thinkers such as Rousseau and Herder
argued that language had originated in the instinctive expression of
emotions, and that it was originally closer to music and poetry than to
the logical expression of rational thought. Rationalist philosophers
such as Kant and Descartes
held the opposite view. Around the turn of the 20th century, thinkers
began to wonder about the role of language in shaping our experiences of
the world – asking whether language simply reflects the objective
structure of the world, or whether it creates concepts that it in turn
imposes on our experience of the objective world. This led to the
question of whether philosophical problems are really firstly linguistic
problems. The resurgence of the view that language plays a significant
role in the creation and circulation of concepts, and that the study of
philosophy is essentially the study of language, is associated with what
has been called the linguistic turn and philosophers such as Wittgenstein
in 20th-century philosophy. These debates about language in relation to
meaning and reference, cognition and consciousness remain active today.
Mental faculty, organ or instinct
One definition sees language primarily as the mental faculty
that allows humans to undertake linguistic behaviour: to learn
languages and to produce and understand utterances. This definition
stresses the universality of language to all humans, and it emphasizes
the biological basis for the human capacity for language as a unique
development of the human brain.
Proponents of the view that the drive to language acquisition is innate
in humans argue that this is supported by the fact that all cognitively
normal children raised in an environment where language is accessible
will acquire language without formal instruction. Languages may even
develop spontaneously in environments where people live or grow up
together without a common language; for example, creole languages and spontaneously developed sign languages such as Nicaraguan Sign Language. This view, which can be traced back to the philosophers Kant and Descartes, understands language to be largely innate, for example, in Chomsky’s theory of Universal Grammar, or American philosopher Jerry Fodor’s extreme innatist theory. These kinds of definitions are often applied in studies of language within a cognitive science framework and in neurolinguistics.[9][10]
Formal symbolic system
Another definition sees language as a formal system
of signs governed by grammatical rules of combination to communicate
meaning. This definition stresses that human languages can be described
as closed structural systems consisting of rules that relate particular signs to particular meanings. This structuralist view of language was first introduced by Ferdinand de Saussure,[12] and his structuralism remains foundational for many approaches to language.[13]
Some proponents of Saussure’s view of language have advocated a
formal approach which studies language structure by identifying its
basic elements and then by presenting a formal account of the rules
according to which the elements combine in order to form words and
sentences. The main proponent of such a theory is Noam Chomsky, the originator of the generative theory of grammar, who has defined language as the construction of sentences that can be generated using transformational grammars. Chomsky considers these rules to be an innate feature of the human mind and to constitute the rudiments of what language is.[15]
By way of contrast, such transformational grammars are also commonly
used to provide formal definitions of language are commonly used in formal logic, in formal theories of grammar, and in applied computational linguistics.[16][17]
In the philosophy of language, the view of linguistic meaning as
residing in the logical relations between propositions and reality was
developed by philosophers such as Alfred Tarski, Bertrand Russell, and other formal logicians.
Tool for communication
Yet another definition sees language as a system of communication
that enables humans to exchange verbal or symbolic utterances. This
definition stresses the social functions of language and the fact that
humans use it to express themselves and to manipulate objects in their
environment. Functional theories of grammar
explain grammatical structures by their communicative functions, and
understand the grammatical structures of language to be the result of an
adaptive process by which grammar was “tailored” to serve the
communicative needs of its users.[18][19]
This view of language is associated with the study of language in pragmatic, cognitive, and interactive frameworks, as well as in sociolinguistics and linguistic anthropology.
Functionalist theories tend to study grammar as dynamic phenomena, as
structures that are always in the process of changing as they are
employed by their speakers. This view places importance on the study of linguistic typology, or the classification of languages according to structural features, as it can be shown that processes of grammaticalization tend to follow trajectories that are partly dependent on typology.[17] In the philosophy of language, the view of pragmatics as being central to language and meaning is often associated with Wittgenstein’s later works and with ordinary language philosophers such as J. L. Austin, Paul Grice, John Searle, and W. O. Quine.
Unique status of human language
A number of features, many of which were described by Charles Hockett and called design features[21] set human language apart from other known systems of communication, such as those used by non-human animals.
Communication systems used by other animals such as bees or apes are closed systems that consist of a finite, usually very limited, number of possible ideas that can be expressed.[22] In contrast, human language is open-ended and productive,
meaning that it allows humans to produce a vast range of utterances
from a finite set of elements, and to create new words and sentences.
This is possible because human language is based on a dual code, in
which a finite number of elements which are meaningless in themselves
(e.g. sounds, letters or gestures) can be combined to form an infinite
number of larger units of meaning (words and sentences).[23]
However, one study has demonstrated that an Australian bird, the
chestnut-crowned babbler, is capable of using the same acoustic elements
in different arrangements to create two functionally distinct
vocalizations. [24]
Additionally, pied babblers have demonstrated the ability to generate
two functionally distinct vocalisations composed of the same sound type,
which can only be distinguished by the number of repeated elements. [25]
Several species of animals have proved to be able to acquire forms of communication through social learning: for instance a bonobo named Kanzi learned to express itself using a set of symbolic lexigrams.
Similarly, many species of birds and whales learn their songs by
imitating other members of their species. However, while some animals
may acquire large numbers of words and symbols,[note 1]
none have been able to learn as many different signs as are generally
known by an average 4 year old human, nor have any acquired anything
resembling the complex grammar of human language.[26]
Human languages also differ from animal communication systems in that they employ grammatical and semantic categories, such as noun and verb, present and past, which may be used to express exceedingly complex meanings.[26] Human language is also unique in having the property of recursivity:
for example, a noun phrase can contain another noun phrase (as in
“[[the chimpanzee]’s lips]”) or a clause can contain another clause (as
in “[I see [the dog is running]]”).[2] Human language is also the only known natural communication system whose adaptability may be referred to as modality independent.
This means that it can be used not only for communication through one
channel or medium, but through several. For example, spoken language
uses the auditive modality, whereas sign languages and writing use the visual modality, and braille writing uses the tactile modality.[27]
Human language is also unique in being able to refer to abstract
concepts and to imagined or hypothetical events as well as events that
took place in the past or may happen in the future. This ability to
refer to events that are not at the same time or place as the speech
event is called displacement, and while some animal communication systems can use displacement (such as the communication of bees
that can communicate the location of sources of nectar that are out of
sight), the degree to which it is used in human language is also
considered unique.[23]
Origin
Theories about the origin of language differ in regard to their basic
assumptions about what language is. Some theories are based on the idea
that language is so complex that one cannot imagine it simply appearing
from nothing in its final form, but that it must have evolved from
earlier pre-linguistic systems among our pre-human ancestors. These
theories can be called continuity-based theories. The opposite viewpoint
is that language is such a unique human trait that it cannot be
compared to anything found among non-humans and that it must therefore
have appeared suddenly in the transition from pre-hominids to early man.
These theories can be defined as discontinuity-based. Similarly,
theories based on Chomsky’s generative view of language see language
mostly as an innate faculty that is largely genetically encoded, whereas
functionalist theories see it as a system that is largely cultural,
learned through social interaction.[29]
One prominent proponent of a discontinuity-based theory of human language origins is linguist and philosopher Noam Chomsky.[29]
Chomsky proposes that “some random mutation took place, maybe after
some strange cosmic ray shower, and it reorganized the brain, implanting
a language organ in an otherwise primate brain.”
Though cautioning against taking this story too literally, Chomsky
insists that “it may be closer to reality than many other fairy tales
that are told about evolutionary processes, including language.”
Continuity-based theories are held by a majority of scholars, but
they vary in how they envision this development. Those who see language
as being mostly innate, for example psychologist Steven Pinker, hold the precedents to be animal cognition,[10] whereas those who see language as a socially learned tool of communication, such as psychologist Michael Tomasello, see it as having developed from animal communication in primates: either gestural or vocal communication to assist in cooperation.[31] Other continuity-based models see language as having developed from music, a view already espoused by Rousseau, Herder, Humboldt, and Charles Darwin. A prominent proponent of this view is archaeologist Steven Mithen. Stephen Anderson states that the age of spoken languages is estimated at 60,000 to 100,000 years[33] and that:
Researchers on the evolutionary origin of language generally find it
plausible to suggest that language was invented only once, and that all
modern spoken languages are thus in some way related, even if that
relation can no longer be recovered … because of limitations on the
methods available for reconstruction.[34]
Because language emerged in the early prehistory
of man, before the existence of any written records, its early
development has left no historical traces, and it is believed that no
comparable processes can be observed today. Theories that stress
continuity often look at animals to see if, for example, primates
display any traits that can be seen as analogous to what pre-human
language must have been like. And early human fossils can be inspected
for traces of physical adaptation to language use or pre-linguistic
forms of symbolic behaviour. Among the signs in human fossils that may
suggest linguistic abilities are: the size of the brain relative to body
mass, the presence of a larynx capable of advanced sound production and the nature of tools and other manufactured artifacts.
It was mostly undisputed that pre-human australopithecines did not have communication systems significantly different from those found in great apes in general. However, a 2017 study on Ardipithecus ramidus challenges this belief.[36] Scholarly opinions vary as to the developments since the appearance of the genus Homo
some 2.5 million years ago. Some scholars assume the development of
primitive language-like systems (proto-language) as early as Homo habilis (2.3 million years ago) while others place the development of primitive symbolic communication only with Homo erectus (1.8 million years ago) or Homo heidelbergensis (0.6 million years ago), and the development of language proper with Anatomically Modern Homo sapiens with the Upper Paleolithic revolution less than 100,000 years ago.
Study
Noam Chomsky is one of the most important linguistic theorists of the 20th century.
The study of language, linguistics, has been developing into a science since the first grammatical descriptions of particular languages in India more than 2000 years ago, after the development of the Brahmi script.
Modern linguistics is a science that concerns itself with all aspects
of language, examining it from all of the theoretical viewpoints
described above.[39]
Subdisciplines
The academic study of language is conducted within many different
disciplinary areas and from different theoretical angles, all of which
inform modern approaches to linguistics. For example, descriptive linguistics examines the grammar of single languages, theoretical linguistics
develops theories on how best to conceptualize and define the nature of
language based on data from the various extant human languages, sociolinguistics
studies how languages are used for social purposes informing in turn
the study of the social functions of language and grammatical
description, neurolinguistics studies how language is processed in the human brain and allows the experimental testing of theories, computational linguistics
builds on theoretical and descriptive linguistics to construct
computational models of language often aimed at processing natural
language or at testing linguistic hypotheses, and historical linguistics
relies on grammatical and lexical descriptions of languages to trace
their individual histories and reconstruct trees of language families by
using the comparative method.[40]
Early history
The formal study of language is often considered to have started in India with Pāṇini, the 5th century BC grammarian who formulated 3,959 rules of Sanskrit morphology. However, Sumerian scribes already studied the differences between Sumerian and Akkadian grammar around 1900 BC. Subsequent grammatical traditions developed in all of the ancient cultures that adopted writing.[41]
In the 17th century AD, the French Port-Royal Grammarians
developed the idea that the grammars of all languages were a reflection
of the universal basics of thought, and therefore that grammar was
universal. In the 18th century, the first use of the comparative method by British philologist and expert on ancient India William Jones sparked the rise of comparative linguistics.[42] The scientific study of language was broadened from Indo-European to language in general by Wilhelm von Humboldt. Early in the 20th century, Ferdinand de Saussure introduced the idea of language as a static system of interconnected units, defined through the oppositions between them.[12]
By introducing a distinction between diachronic and synchronic
analyses of language, he laid the foundation of the modern discipline
of linguistics. Saussure also introduced several basic dimensions of
linguistic analysis that are still fundamental in many contemporary
linguistic theories, such as the distinctions between syntagm and paradigm, and the Langue-parole distinction, distinguishing language as an abstract system (langue), from language as a concrete manifestation of this system (parole).[43]
Contemporary linguistics
In the 1960s, Noam Chomsky formulated the generative theory of language.
According to this theory, the most basic form of language is a set of
syntactic rules that is universal for all humans and which underlies the
grammars of all human languages. This set of rules is called Universal Grammar;
for Chomsky, describing it is the primary objective of the discipline
of linguistics. Thus, he considered that the grammars of individual
languages are only of importance to linguistics insofar as they allow us
to deduce the universal underlying rules from which the observable
linguistic variability is generated.[44]
In opposition to the formal theories of the generative school, functional theories of language
propose that since language is fundamentally a tool, its structures are
best analyzed and understood by reference to their functions. Formal theories of grammar
seek to define the different elements of language and describe the way
they relate to each other as systems of formal rules or operations,
while functional theories seek to define the functions performed by
language and then relate them to the linguistic elements that carry them
out.[17][note 2] The framework of cognitive linguistics
interprets language in terms of the concepts (which are sometimes
universal, and sometimes specific to a particular language) which
underlie its forms. Cognitive linguistics is primarily concerned with
how the mind creates meaning through language.[45]
Physiological and neural architecture of language and speech
Speaking is the default modality for language in all cultures. The
production of spoken language depends on sophisticated capacities for
controlling the lips, tongue and other components of the vocal
apparatus, the ability to acoustically decode speech sounds, and the
neurological apparatus required for acquiring and producing language.[46] The study of the genetic bases for human language is at an early stage: the only gene that has definitely been implicated in language production is FOXP2, which may cause a kind of congenital language disorder if affected by mutations.[47]
The brain
The brain is the coordinating center of all linguistic activity; it
controls both the production of linguistic cognition and of meaning and
the mechanics of speech production. Nonetheless, our knowledge of the
neurological bases for language is quite limited, though it has advanced
considerably with the use of modern imaging techniques. The discipline
of linguistics dedicated to studying the neurological aspects of
language is called neurolinguistics.[48]
Early work in neurolinguistics involved the study of language in
people with brain lesions, to see how lesions in specific areas affect
language and speech. In this way, neuroscientists in the 19th century
discovered that two areas in the brain are crucially implicated in
language processing. The first area is Wernicke’s area, which is located in the posterior section of the superior temporal gyrus in the dominant cerebral hemisphere. People with a lesion in this area of the brain develop receptive aphasia,
a condition in which there is a major impairment of language
comprehension, while speech retains a natural-sounding rhythm and a
relatively normal sentence structure. The second area is Broca’s area, located in the posterior inferior frontal gyrus of the dominant hemisphere. People with a lesion to this area develop expressive aphasia, meaning that they know what they want to say, they just cannot get it out.[49]
They are typically able to understand what is being said to them, but
unable to speak fluently. Other symptoms that may be present in
expressive aphasia include problems with fluency, articulation,
word-finding, word repetition,
and producing and comprehending complex grammatical sentences, both
orally and in writing. Those with this aphasia also exhibit
ungrammatical speech and show inability to use syntactic information to
determine the meaning of sentences. Both expressive and receptive
aphasia also affect the use of sign language, in analogous ways to how
they affect speech, with expressive aphasia causing signers to sign
slowly and with incorrect grammar, whereas a signer with receptive
aphasia will sign fluently, but make little sense to others and have
difficulties comprehending others’ signs. This shows that the impairment
is specific to the ability to use language, not to the physiology used
for speech production.[50][51]
With technological advances in the late 20th century, neurolinguists have also incorporated non-invasive techniques such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electrophysiology to study language processing in individuals without impairments.[48]
Anatomy of speech
Spectrogram of American English vowels [i, u, ɑ] showing the formants f1 and f2
Real time MRI scan of a person speaking in Mandarin Chinese
Spoken language relies on human physical ability to produce sound, which is a longitudinal wave propagated through the air at a frequency capable of vibrating the ear drum. This ability depends on the physiology of the human speech organs. These organs consist of the lungs, the voice box (larynx),
and the upper vocal tract – the throat, the mouth, and the nose. By
controlling the different parts of the speech apparatus, the airstream
can be manipulated to produce different speech sounds.[52]
The sound of speech can be analyzed into a combination of segmental and suprasegmental
elements. The segmental elements are those that follow each other in
sequences, which are usually represented by distinct letters in
alphabetic scripts, such as the Roman script. In free flowing speech,
there are no clear boundaries between one segment and the next, nor
usually are there any audible pauses between words. Segments therefore
are distinguished by their distinct sounds which are a result of their
different articulations, and they can be either vowels or consonants.
Suprasegmental phenomena encompass such elements as stress, phonation type, voice timbre, and prosody or intonation, all of which may have effects across multiple segments.[53]
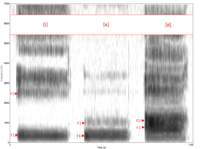
Consonants and vowel segments combine to form syllables, which in turn combine to form utterances; these can be distinguished phonetically as the space between two inhalations. Acoustically, these different segments are characterized by different formant structures, that are visible in a spectrogram
of the recorded sound wave (See illustration of Spectrogram of the
formant structures of three English vowels). Formants are the amplitude
peaks in the frequency spectrum of a specific sound.[53][54]
Vowels are those sounds that have no audible friction caused by the
narrowing or obstruction of some part of the upper vocal tract. They
vary in quality according to the degree of lip aperture and the
placement of the tongue within the oral cavity.[53] Vowels are called close when the lips are relatively closed, as in the pronunciation of the vowel [i] (English “ee”), or open when the lips are relatively open, as in the vowel [a] (English “ah”). If the tongue is located towards the back of the mouth, the quality changes, creating vowels such as [u] (English “oo”). The quality also changes depending on whether the lips are rounded as opposed to unrounded, creating distinctions such as that between [i] (unrounded front vowel such as English “ee”) and [y] (rounded front vowel such as German “ü”).[55]
Consonants are those sounds that have audible friction or closure at
some point within the upper vocal tract. Consonant sounds vary by place
of articulation, i.e. the place in the vocal tract where the airflow is
obstructed, commonly at the lips, teeth, alveolar ridge, palate, velum, uvula, or glottis. Each place of articulation produces a different set of consonant sounds, which are further distinguished by manner of articulation, or the kind of friction, whether full closure, in which case the consonant is called occlusive or stop, or different degrees of aperture creating fricatives and approximants. Consonants can also be either voiced or unvoiced,
depending on whether the vocal cords are set in vibration by airflow
during the production of the sound. Voicing is what separates English [s] in bus (unvoiced sibilant) from [z] in buzz (voiced sibilant).[56]
Some speech sounds, both vowels and consonants, involve release of air flow through the nasal cavity, and these are called nasals or nasalized sounds. Other sounds are defined by the way the tongue moves within the mouth: such as the l-sounds (called laterals, because the air flows along both sides of the tongue), and the r-sounds (called rhotics) that are characterized by how the tongue is positioned relative to the air stream.[54]
By using these speech organs, humans can produce hundreds of distinct
sounds: some appear very often in the world’s languages, whereas others
are much more common in certain language families, language areas, or
even specific to a single language.[57]
Structure
When described as a system of symbolic communication, language is traditionally seen as consisting of three parts: signs, meanings, and a code connecting signs with their meanings. The study of the process of semiosis, how signs and meanings are combined, used, and interpreted is called semiotics.
Signs can be composed of sounds, gestures, letters, or symbols,
depending on whether the language is spoken, signed, or written, and
they can be combined into complex signs, such as words and phrases. When
used in communication, a sign is encoded and transmitted by a sender
through a channel to a receiver who decodes it.[58]
Some of the properties that define human language as opposed to other
communication systems are: the arbitrariness of the linguistic sign,
meaning that there is no predictable connection between a linguistic
sign and its meaning; the duality of the linguistic system, meaning that
linguistic structures are built by combining elements into larger
structures that can be seen as layered, e.g. how sounds build words and
words build phrases; the discreteness of the elements of language,
meaning that the elements out of which linguistic signs are constructed
are discrete units, e.g. sounds and words, that can be distinguished
from each other and rearranged in different patterns; and the
productivity of the linguistic system, meaning that the finite number of
linguistic elements can be combined into a theoretically infinite
number of combinations.[58]
The rules by which signs can be combined to form words and phrases are called syntax or grammar. The meaning that is connected to individual signs, morphemes, words, phrases, and texts is called semantics.[59]
The division of language into separate but connected systems of sign
and meaning goes back to the first linguistic studies of de Saussure and
is now used in almost all branches of linguistics.[60]
Semantics
Languages express meaning by relating a sign form to a meaning, or
its content. Sign forms must be something that can be perceived, for
example, in sounds, images, or gestures, and then related to a specific
meaning by social convention. Because the basic relation of meaning for
most linguistic signs is based on social convention, linguistic signs
can be considered arbitrary, in the sense that the convention is
established socially and historically, rather than by means of a natural
relation between a specific sign form and its meaning.
Thus, languages must have a vocabulary of signs related to specific meaning. The English sign “dog” denotes, for example, a member of the species Canis familiaris. In a language, the array of arbitrary signs connected to specific meanings is called the lexicon, and a single sign connected to a meaning is called a lexeme.
Not all meanings in a language are represented by single words. Often,
semantic concepts are embedded in the morphology or syntax of the
language in the form of grammatical categories.[61]
All languages contain the semantic structure of predication:
a structure that predicates a property, state, or action.
Traditionally, semantics has been understood to be the study of how
speakers and interpreters assign truth values
to statements, so that meaning is understood to be the process by which
a predicate can be said to be true or false about an entity, e.g. “[x
[is y]]” or “[x [does y]]”. Recently, this model of semantics has been
complemented with more dynamic models of meaning that incorporate shared
knowledge about the context in which a sign is interpreted into the
production of meaning. Such models of meaning are explored in the field
of pragmatics.[61]
Sounds and symbols
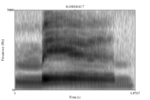
A spectrogram showing the sound of the spoken English word “man”, which is written phonetically as [mæn].
Note that in flowing speech, there is no clear division between
segments, only a smooth transition as the vocal apparatus moves.
The syllable “wi” in the Hangul script
Depending on modality, language structure can be based on systems of
sounds (speech), gestures (sign languages), or graphic or tactile
symbols (writing). The ways in which languages use sounds or signs to
construct meaning are studied in phonology.[62] The study of how humans produce and perceive vocal sounds is called phonetics.[63]
In spoken language, meaning is produced when sounds become part of a
system in which some sounds can contribute to expressing meaning and
others do not. In any given language, only a limited number of the many
distinct sounds that can be created by the human vocal apparatus
contribute to constructing meaning.[57]
Sounds as part of a linguistic system are called phonemes.[64]
Phonemes are abstract units of sound, defined as the smallest units in a
language that can serve to distinguish between the meaning of a pair of
minimally different words, a so-called minimal pair. In English, for example, the words bat [bæt] and pat [pʰæt] form a minimal pair, in which the distinction between /b/ and /p/
differentiates the two words, which have different meanings. However,
each language contrasts sounds in different ways. For example, in a
language that does not distinguish between voiced and unvoiced
consonants, the sounds [p] and [b]
(if they both occur) could be considered a single phoneme, and
consequently, the two pronunciations would have the same meaning.
Similarly, the English language does not distinguish phonemically
between aspirated and non-aspirated pronunciations of consonants, as many other languages like Korean and Hindi do: the unaspirated /p/ in spin [spɪn] and the aspirated /p/ in pin [pʰɪn] are considered to be merely different ways of pronouncing the same phoneme (such variants of a single phoneme are called allophones), whereas in Mandarin Chinese, the same difference in pronunciation distinguishes between the words [pʰá] ‘crouch’ and [pá] ‘eight’ (the accent above the á means that the vowel is pronounced with a high tone).[65]
All spoken languages have phonemes of at least two different categories, vowels and consonants, that can be combined to form syllables.[53]
As well as segments such as consonants and vowels, some languages also
use sound in other ways to convey meaning. Many languages, for example,
use stress, pitch, duration, and tone to distinguish meaning. Because these phenomena operate outside of the level of single segments, they are called suprasegmental.[66] Some languages have only a few phonemes, for example, Rotokas and Pirahã language with 11 and 10 phonemes respectively, whereas languages like Taa may have as many as 141 phonemes.[65] In sign languages, the equivalent to phonemes (formerly called cheremes)
are defined by the basic elements of gestures, such as hand shape,
orientation, location, and motion, which correspond to manners of
articulation in spoken language.[67][68][69]
Writing systems represent language using visual symbols, which may or may not correspond to the sounds of spoken language. The Latin alphabet
(and those on which it is based or that have been derived from it) was
originally based on the representation of single sounds, so that words
were constructed from letters that generally denote a single consonant
or vowel in the structure of the word. In syllabic scripts, such as the Inuktitut syllabary, each sign represents a whole syllable. In logographic scripts, each sign represents an entire word,[70] and will generally bear no relation to the sound of that word in spoken language.
Because all languages have a very large number of words, no purely
logographic scripts are known to exist. Written language represents the
way spoken sounds and words follow one after another by arranging
symbols according to a pattern that follows a certain direction. The
direction used in a writing system is entirely arbitrary and established
by convention. Some writing systems use the horizontal axis (left to
right as the Latin script or right to left as the Arabic script),
while others such as traditional Chinese writing use the vertical
dimension (from top to bottom). A few writing systems use opposite
directions for alternating lines, and others, such as the ancient Maya
script, can be written in either direction and rely on graphic cues to
show the reader the direction of reading.[71]
In order to represent the sounds of the world’s languages in writing, linguists have developed the International Phonetic Alphabet, designed to represent all of the discrete sounds that are known to contribute to meaning in human languages.[72]
Grammar
Grammar is the study of how meaningful elements called morphemes within a language can be combined into utterances. Morphemes can either be free or bound. If they are free to be moved around within an utterance, they are usually called words, and if they are bound to other words or morphemes, they are called affixes.
The way in which meaningful elements can be combined within a language
is governed by rules. The rules for the internal structure of words are
called morphology. The rules of the internal structure of phrases and sentences are called syntax.[73]
Grammatical categories
Grammar can be described as a system of categories and a set of rules
that determine how categories combine to form different aspects of
meaning.[74]
Languages differ widely in whether they are encoded through the use of
categories or lexical units. However, several categories are so common
as to be nearly universal. Such universal categories include the
encoding of the grammatical relations of participants and predicates by
grammatically distinguishing between their relations to a predicate, the encoding of temporal and spatial relations on predicates, and a system of grammatical person governing reference to and distinction between speakers and addressees and those about whom they are speaking.[75]
Word classes
Languages organize their parts of speech
into classes according to their functions and positions relative to
other parts. All languages, for instance, make a basic distinction
between a group of words that prototypically denotes things and concepts
and a group of words that prototypically denotes actions and events.
The first group, which includes English words such as “dog” and “song”,
are usually called nouns. The second, which includes “run” and “sing”, are called verbs. Another common category is the adjective:
words that describe properties or qualities of nouns, such as “red” or
“big”. Word classes can be “open” if new words can continuously be added
to the class, or relatively “closed” if there is a fixed number of
words in a class. In English, the class of pronouns is closed, whereas
the class of adjectives is open, since an infinite number of adjectives
can be constructed from verbs (e.g. “saddened”) or nouns (e.g. with the
-like suffix, as in “noun-like”). In other languages such as Korean, the situation is the opposite, and new pronouns can be constructed, whereas the number of adjectives is fixed.[76]
Word classes also carry out differing functions in grammar. Prototypically, verbs are used to construct predicates, while nouns are used as arguments
of predicates. In a sentence such as “Sally runs”, the predicate is
“runs”, because it is the word that predicates a specific state about
its argument “Sally”. Some verbs such as “curse” can take two arguments,
e.g. “Sally cursed John”. A predicate that can only take a single
argument is called intransitive, while a predicate that can take two arguments is called transitive.[77]
Many other word classes exist in different languages, such as conjunctions like “and” that serve to join two sentences, articles that introduce a noun, interjections such as “wow!”, or ideophones
like “splash” that mimic the sound of some event. Some languages have
positionals that describe the spatial position of an event or entity.
Many languages have classifiers that identify countable nouns as belonging to a particular type or having a particular shape. For instance, in Japanese, the general noun classifier for humans is nin (人), and it is used for counting humans, whatever they are called:[78]
- san-nin no gakusei (三人の学生) lit. “3 human-classifier of student” — three students
For trees, it would be:
- san-bon no ki (三本の木) lit. “3 classifier-for-long-objects of tree” — three trees
Morphology
In linguistics, the study of the internal structure of complex words and the processes by which words are formed is called morphology. In most languages, it is possible to construct complex words that are built of several morphemes.
For instance, the English word “unexpected” can be analyzed as being
composed of the three morphemes “un-”, “expect” and “-ed”.[79]
Morphemes can be classified according to whether they are independent morphemes, so-called roots, or whether they can only co-occur attached to other morphemes. These bound morphemes or affixes can be classified according to their position in relation to the root: prefixes precede the root, suffixes follow the root, and infixes
are inserted in the middle of a root. Affixes serve to modify or
elaborate the meaning of the root. Some languages change the meaning of
words by changing the phonological structure of a word, for example, the
English word “run”, which in the past tense is “ran”. This process is
called ablaut. Furthermore, morphology distinguishes between the process of inflection, which modifies or elaborates on a word, and the process of derivation,
which creates a new word from an existing one. In English, the verb
“sing” has the inflectional forms “singing” and “sung”, which are both
verbs, and the derivational form “singer”, which is a noun derived from
the verb with the agentive suffix “-er”.[80]
Languages differ widely in how much they rely on morphological
processes of word formation. In some languages, for example, Chinese,
there are no morphological processes, and all grammatical information is
encoded syntactically by forming strings of single words. This type of
morpho-syntax is often called isolating,
or analytic, because there is almost a full correspondence between a
single word and a single aspect of meaning. Most languages have words
consisting of several morphemes, but they vary in the degree to which
morphemes are discrete units. In many languages, notably in most
Indo-European languages, single morphemes may have several distinct
meanings that cannot be analyzed into smaller segments. For example, in
Latin, the word bonus, or “good”, consists of the root bon-, meaning “good”, and the suffix -us, which indicates masculine gender, singular number, and nominative case. These languages are called fusional languages, because several meanings may be fused into a single morpheme. The opposite of fusional languages are agglutinative languages
which construct words by stringing morphemes together in chains, but
with each morpheme as a discrete semantic unit. An example of such a
language is Turkish, where for example, the word evlerinizden, or “from your houses”, consists of the morphemes, ev-ler-iniz-den with the meanings house-plural-your-from. The languages that rely on morphology to the greatest extent are traditionally called polysynthetic languages. They may express the equivalent of an entire English sentence in a single word. For example, in Persian the single word nafahmidamesh means I didn’t understand it consisting of morphemes na-fahm-id-am-esh with the meanings, “negation.understand.past.I.it”. As another example with more complexity, in the Yupik word tuntussuqatarniksatengqiggtuq, which means “He had not yet said again that he was going to hunt reindeer”, the word consists of the morphemes tuntu-ssur-qatar-ni-ksaite-ngqiggte-uq with the meanings, “reindeer-hunt-future-say-negation-again-third.person.singular.indicative”, and except for the morpheme tuntu (”reindeer”) none of the other morphemes can appear in isolation.[81]
Many languages use morphology to cross-reference words within a sentence. This is sometimes called agreement.
For example, in many Indo-European languages, adjectives must
cross-reference the noun they modify in terms of number, case, and
gender, so that the Latin adjective bonus, or “good”, is
inflected to agree with a noun that is masculine gender, singular
number, and nominative case. In many polysynthetic languages, verbs
cross-reference their subjects and objects. In these types of languages,
a single verb may include information that would require an entire
sentence in English. For example, in the Basque phrase ikusi nauzu, or “you saw me”, the past tense auxiliary verb n-au-zu (similar to English “do”) agrees with both the subject (you) expressed by the n- prefix, and with the object (me) expressed by the – zu suffix. The sentence could be directly transliterated as “see you-did-me”[82]
Syntax
In addition to word classes, a sentence can be analyzed in terms of grammatical functions: “The cat” is the subject of the phrase, “on the mat” is a locative phrase, and “sat” is the core of the predicate.
Another way in which languages convey meaning is through the order of
words within a sentence. The grammatical rules for how to produce new
sentences from words that are already known is called syntax. The
syntactical rules of a language determine why a sentence in English such
as “I love you” is meaningful, but “*love you I” is not.[note 3]
Syntactical rules determine how word order and sentence structure is
constrained, and how those constraints contribute to meaning.[83]
For example, in English, the two sentences “the slaves were cursing the
master” and “the master was cursing the slaves” mean different things,
because the role of the grammatical subject is encoded by the noun being
in front of the verb, and the role of object is encoded by the noun
appearing after the verb. Conversely, in Latin, both Dominus servos vituperabat and Servos vituperabat dominus mean “the master was reprimanding the slaves”, because servos, or “slaves”, is in the accusative case, showing that they are the grammatical object of the sentence, and dominus, or “master”, is in the nominative case, showing that he is the subject.[84]
Latin uses morphology to express the distinction between subject and
object, whereas English uses word order. Another example of how
syntactic rules contribute to meaning is the rule of inverse word order in questions,
which exists in many languages. This rule explains why when in English,
the phrase “John is talking to Lucy” is turned into a question, it
becomes “Who is John talking to?”, and not “John is talking to who?”.
The latter example may be used as a way of placing special emphasis
on “who”, thereby slightly altering the meaning of the question. Syntax
also includes the rules for how complex sentences are structured by
grouping words together in units, called phrases,
that can occupy different places in a larger syntactic structure.
Sentences can be described as consisting of phrases connected in a tree
structure, connecting the phrases to each other at different levels.
To the right is a graphic representation of the syntactic analysis of
the English sentence “the cat sat on the mat”. The sentence is analyzed
as being constituted by a noun phrase, a verb, and a prepositional
phrase; the prepositional phrase is further divided into a preposition
and a noun phrase, and the noun phrases consist of an article and a
noun.[86]
The reason sentences can be seen as being composed of phrases is
because each phrase would be moved around as a single element if
syntactic operations were carried out. For example, “the cat” is one
phrase, and “on the mat” is another, because they would be treated as
single units if a decision was made to emphasize the location by moving
forward the prepositional phrase: “[And] on the mat, the cat sat”.[86]
There are many different formalist and functionalist frameworks that
propose theories for describing syntactic structures, based on different
assumptions about what language is and how it should be described. Each
of them would analyze a sentence such as this in a different manner.[17]
Typology and universals
Languages can be classified in relation to their grammatical types.
Languages that belong to different families nonetheless often have
features in common, and these shared features tend to correlate.[87] For example, languages can be classified on the basis of their basic word order, the relative order of the verb, and its constituents in a normal indicative sentence. In English, the basic order is SVO: “The snake(S) bit(V) the man(O)”, whereas for example, the corresponding sentence in the Australian language Gamilaraay would be d̪uyugu n̪ama d̪ayn yiːy (snake man bit), SOV.[88]
Word order type is relevant as a typological parameter, because basic
word order type corresponds with other syntactic parameters, such as the
relative order of nouns and adjectives, or of the use of prepositions or postpositions. Such correlations are called implicational universals.[89] For example, most (but not all) languages that are of the SOV type have postpositions rather than prepositions, and have adjectives before nouns.[90]
All languages structure sentences into Subject, Verb, and Object, but
languages differ in the way they classify the relations between actors
and actions. English uses the nominative-accusative
word typology: in English transitive clauses, the subjects of both
intransitive sentences (”I run”) and transitive sentences (”I love you”)
are treated in the same way, shown here by the nominative pronoun I. Some languages, called ergative,
Gamilaraay among them, distinguish instead between Agents and Patients.
In ergative languages, the single participant in an intransitive
sentence, such as “I run”, is treated the same as the patient in a
transitive sentence, giving the equivalent of “me run”. Only in
transitive sentences would the equivalent of the pronoun “I” be used.[88]
In this way the semantic roles can map onto the grammatical relations
in different ways, grouping an intransitive subject either with Agents
(accusative type) or Patients (ergative type) or even making each of the
three roles differently, which is called the tripartite type.[91]
The shared features of languages which belong to the same typological
class type may have arisen completely independently. Their
co-occurrence might be due to universal laws governing the structure of
natural languages, “language universals”, or they might be the result of
languages evolving convergent solutions to the recurring communicative
problems that humans use language to solve.[18]
Social contexts of use and transmission
While humans have the ability to learn any language, they only do so
if they grow up in an environment in which language exists and is used
by others. Language is therefore dependent on communities of speakers in which children learn language
from their elders and peers and themselves transmit language to their
own children. Languages are used by those who speak them to communicate and to solve a plethora of social tasks. Many aspects of language use can be seen to be adapted specifically to these purposes.[18]
Due to the way in which language is transmitted between generations and
within communities, language perpetually changes, diversifying into new
languages or converging due to language contact. The process is similar to the process of evolution, where the process of descent with modification leads to the formation of a phylogenetic tree.[93]
However, languages differ from biological organisms in that they
readily incorporate elements from other languages through the process of
diffusion, as speakers of different languages come into contact. Humans also frequently speak more than one language, acquiring their first language
or languages as children, or learning new languages as they grow up.
Because of the increased language contact in the globalizing world, many
small languages are becoming endangered
as their speakers shift to other languages that afford the possibility
to participate in larger and more influential speech communities.[94]
Usage and meaning
The semantic study of meaning assumes that meaning is located in a
relation between signs and meanings that are firmly established through
social convention. However, semantics does not study the way in which
social conventions are made and affect language. Rather, when studying
the way in which words and signs are used, it is often the case that
words have different meanings, depending on the social context of use.
An important example of this is the process called deixis,
which describes the way in which certain words refer to entities
through their relation between a specific point in time and space when
the word is uttered. Such words are, for example, the word, “I” (which
designates the person speaking), “now” (which designates the moment of
speaking), and “here” (which designates the position of speaking). Signs
also change their meanings over time, as the conventions governing
their usage gradually change. The study of how the meaning of linguistic
expressions changes depending on context is called pragmatics. Deixis
is an important part of the way that we use language to point out
entities in the world.[95]
Pragmatics is concerned with the ways in which language use is
patterned and how these patterns contribute to meaning. For example, in
all languages, linguistic expressions can be used not just to transmit
information, but to perform actions. Certain actions are made only
through language, but nonetheless have tangible effects, e.g. the act of
“naming”, which creates a new name for some entity, or the act of
“pronouncing someone man and wife”, which creates a social contract of
marriage. These types of acts are called speech acts, although they can also be carried out through writing or hand signing.[96]
The form of linguistic expression often does not correspond to the
meaning that it actually has in a social context. For example, if at a
dinner table a person asks, “Can you reach the salt?”, that is, in fact,
not a question about the length of the arms of the one being addressed,
but a request to pass the salt across the table. This meaning is
implied by the context in which it is spoken; these kinds of effects of
meaning are called conversational implicatures.
These social rules for which ways of using language are considered
appropriate in certain situations and how utterances are to be
understood in relation to their context vary between communities, and
learning them is a large part of acquiring communicative competence in a language.[97]
Acquisition
All healthy, normally developing
human beings learn to use language. Children acquire the language or
languages used around them: whichever languages they receive sufficient
exposure to during childhood. The development is essentially the same
for children acquiring sign or oral languages.[98]
This learning process is referred to as first-language acquisition,
since unlike many other kinds of learning, it requires no direct
teaching or specialized study. In The Descent of Man, naturalist Charles Darwin called this process “an instinctive tendency to acquire an art”.[10]
First language acquisition proceeds in a fairly regular sequence,
though there is a wide degree of variation in the timing of particular
stages among normally developing infants. From birth, newborns respond
more readily to human speech than to other sounds. Around one month of
age, babies appear to be able to distinguish between different speech sounds. Around six months of age, a child will begin babbling, producing the speech sounds or handshapes of the languages used around them. Words appear around the age of 12 to 18 months; the average vocabulary of an eighteen-month-old child is around 50 words. A child’s first utterances are holophrases
(literally “whole-sentences”), utterances that use just one word to
communicate some idea. Several months after a child begins producing
words, he or she will produce two-word utterances, and within a few more
months will begin to produce telegraphic speech, or short sentences that are less grammatically
complex than adult speech, but that do show regular syntactic
structure. From roughly the age of three to five years, a child’s
ability to speak or sign is refined to the point that it resembles adult
language.[99][100] Studies published in 2013 have indicated that unborn fetuses are capable of language acquisition to some degree.[101][102]
Acquisition of second and additional languages can come at any age,
through exposure in daily life or courses. Children learning a second
language are more likely to achieve native-like fluency than adults, but
in general, it is very rare for someone speaking a second language to
pass completely for a native speaker. An important difference between
first language acquisition and additional language acquisition is that
the process of additional language acquisition is influenced by
languages that the learner already knows.[103]
Culture
Languages, understood as the particular set of speech norms of a
particular community, are also a part of the larger culture of the
community that speaks them. Languages differ not only in pronunciation,
vocabulary, and grammar, but also through having different “cultures of
speaking.” Humans use language as a way of signalling identity with one
cultural group as well as difference from others. Even among speakers of
one language, several different ways of using the language exist, and
each is used to signal affiliation with particular subgroups within a
larger culture. Linguists and anthropologists, particularly sociolinguists, ethnolinguists, and linguistic anthropologists have specialized in studying how ways of speaking vary between speech communities.[104]
Linguists use the term “varieties” to refer to the different ways of speaking a language. This term includes geographically or socioculturally defined dialects as well as the jargons or styles of subcultures.
Linguistic anthropologists and sociologists of language define
communicative style as the ways that language is used and understood
within a particular culture.[105]
Because norms for language use are shared by members of a specific
group, communicative style also becomes a way of displaying and
constructing group identity. Linguistic differences may become salient
markers of divisions between social groups, for example, speaking a
language with a particular accent may imply membership of an ethnic
minority or social class, one’s area of origin, or status as a second
language speaker. These kinds of differences are not part of the
linguistic system, but are an important part of how people use language
as a social tool for constructing groups.[106]
However, many languages also have grammatical conventions that signal
the social position of the speaker in relation to others through the
use of registers that are related to social hierarchies or divisions. In
many languages, there are stylistic or even grammatical differences
between the ways men and women speak, between age groups, or between social classes, just as some languages employ different words depending on who is listening. For example, in the Australian language Dyirbal, a married man must use a special set of words to refer to everyday items when speaking in the presence of his mother-in-law.[107] Some cultures, for example, have elaborate systems of “social deixis“, or systems of signalling social distance through linguistic means.[108]
In English, social deixis is shown mostly through distinguishing
between addressing some people by first name and others by surname, and
in titles such as “Mrs.”, “boy”, “Doctor”, or “Your Honor”, but in other
languages, such systems may be highly complex and codified in the
entire grammar and vocabulary of the language. For instance, in
languages of east Asia such as Thai, Burmese, and Javanese,
different words are used according to whether a speaker is addressing
someone of higher or lower rank than oneself in a ranking system with
animals and children ranking the lowest and gods and members of royalty
as the highest.[108]
Writing, literacy and technology
Throughout history a number of different ways of representing language in graphic media have been invented. These are called writing systems.
The use of writing has made language even more useful to humans. It
makes it possible to store large amounts of information outside of the
human body and retrieve it again, and it allows communication across
distances that would otherwise be impossible. Many languages
conventionally employ different genres, styles, and registers in written
and spoken language, and in some communities, writing traditionally
takes place in an entirely different language than the one spoken. There
is some evidence that the use of writing also has effects on the
cognitive development of humans, perhaps because acquiring literacy
generally requires explicit and formal education.[109]
The invention of the first writing systems is roughly contemporary with the beginning of the Bronze Age in the late 4th millennium BC. The Sumerian archaic cuneiform script and the Egyptian hieroglyphs
are generally considered to be the earliest writing systems, both
emerging out of their ancestral proto-literate symbol systems from
3400–3200 BC with the earliest coherent texts from about 2600 BC.
It is generally agreed that Sumerian writing was an independent
invention; however, it is debated whether Egyptian writing was developed
completely independently of Sumerian, or was a case of cultural diffusion. A similar debate exists for the Chinese script, which developed around 1200 BC. The pre-Columbian Mesoamerican writing systems (including among others Olmec and Maya scripts) are generally believed to have had independent origins.[71]
Change
The first page of the poem Beowulf, written in Old English
in the early medieval period (800–1100 AD). Although Old English is the
direct ancestor of modern English, it is unintelligible to contemporary
English speakers.
All languages change as speakers adopt or invent new ways of speaking
and pass them on to other members of their speech community. Language
change happens at all levels from the phonological level to the levels
of vocabulary, morphology, syntax, and discourse. Even though language
change is often initially evaluated negatively by speakers of the
language who often consider changes to be “decay” or a sign of slipping
norms of language usage, it is natural and inevitable.[110]
Changes may affect specific sounds or the entire phonological system. Sound change can consist of the replacement of one speech sound or phonetic feature
by another, the complete loss of the affected sound, or even the
introduction of a new sound in a place where there had been none. Sound
changes can be conditioned in which case a sound is changed only
if it occurs in the vicinity of certain other sounds. Sound change is
usually assumed to be regular, which means that it is expected to
apply mechanically whenever its structural conditions are met,
irrespective of any non-phonological factors. On the other hand, sound
changes can sometimes be sporadic, affecting only one particular word or a few words, without any seeming regularity. Sometimes a simple change triggers a chain shift in which the entire phonological system is affected. This happened in the Germanic languages when the sound change known as Grimm’s law affected all the stop consonants in the system. The original consonant *bʰ became /b/ in the Germanic languages, the previous *b in turn became /p/, and the previous *p became /f/. The same process applied to all stop consonants and explains why Italic languages such as Latin have p in words like pater and pisces, whereas Germanic languages, like English, have father and fish.[111]
Another example is the Great Vowel Shift
in English, which is the reason that the spelling of English vowels do
not correspond well to their current pronunciation. This is because the
vowel shift brought the already established orthography out of
synchronization with pronunciation. Another source of sound change is
the erosion of words as pronunciation gradually becomes increasingly
indistinct and shortens words, leaving out syllables or sounds. This
kind of change caused Latin mea domina to eventually become the French madame and American English ma’am.[112]
Change also happens in the grammar of languages as discourse patterns such as idioms or particular constructions become grammaticalized.
This frequently happens when words or morphemes erode and the
grammatical system is unconsciously rearranged to compensate for the
lost element. For example, in some varieties of Caribbean Spanish the final /s/ has eroded away. Since Standard Spanish uses final /s/ in the morpheme marking the second person subject “you” in verbs, the Caribbean varieties now have to express the second person using the pronoun tú. This means that the sentence “what’s your name” is ¿como te llamas? [ˈkomo te ˈjamas] in Standard Spanish, but [ˈkomo ˈtu te ˈjama] in Caribbean Spanish. The simple sound change has affected both morphology and syntax.[113]
Another common cause of grammatical change is the gradual petrification
of idioms into new grammatical forms, for example, the way the English
“going to” construction lost its aspect of movement and in some
varieties of English has almost become a full-fledged future tense (e.g.
I’m gonna).
Language change may be motivated by “language internal” factors, such
as changes in pronunciation motivated by certain sounds being difficult
to distinguish aurally or to produce, or through patterns of change
that cause some rare types of constructions to drift towards more common types.[114]
Other causes of language change are social, such as when certain
pronunciations become emblematic of membership in certain groups, such
as social classes, or with ideologies,
and therefore are adopted by those who wish to identify with those
groups or ideas. In this way, issues of identity and politics can have
profound effects on language structure.[115]
Contact
One important source of language change is contact and resulting diffusion of linguistic traits between languages. Language contact occurs when speakers of two or more languages or varieties interact on a regular basis.[116] Multilingualism is likely to have been the norm throughout human history and most people in the modern world are multilingual. Before the rise of the concept of the ethno-national state,
monolingualism was characteristic mainly of populations inhabiting
small islands. But with the ideology that made one people, one state,
and one language the most desirable political arrangement,
monolingualism started to spread throughout the world. Nonetheless,
there are only 250 countries in the world corresponding to some 6000
languages, which means that most countries are multilingual and most
languages therefore exist in close contact with other languages.[117]
When speakers of different languages interact closely, it is typical
for their languages to influence each other. Through sustained language
contact over long periods, linguistic traits diffuse between languages,
and languages belonging to different families may converge to become
more similar. In areas where many languages are in close contact, this
may lead to the formation of language areas
in which unrelated languages share a number of linguistic features. A
number of such language areas have been documented, among them, the Balkan language area, the Mesoamerican language area, and the Ethiopian language area. Also, larger areas such as South Asia, Europe, and Southeast Asia have sometimes been considered language areas, because of widespread diffusion of specific areal features.[118][119]
Language contact may also lead to a variety of other linguistic phenomena, including language convergence, borrowing, and relexification
(replacement of much of the native vocabulary with that of another
language). In situations of extreme and sustained language contact, it
may lead to the formation of new mixed languages that cannot be considered to belong to a single language family. One type of mixed language called pidgins
occurs when adult speakers of two different languages interact on a
regular basis, but in a situation where neither group learns to speak
the language of the other group fluently. In such a case, they will
often construct a communication form that has traits of both languages,
but which has a simplified grammatical and phonological structure. The
language comes to contain mostly the grammatical and phonological
categories that exist in both languages. Pidgin languages are defined by
not having any native speakers, but only being spoken by people who
have another language as their first language. But if a Pidgin language
becomes the main language of a speech community, then eventually
children will grow up learning the pidgin as their first language. As
the generation of child learners grow up, the pidgin will often be seen
to change its structure and acquire a greater degree of complexity. This
type of language is generally called a creole language. An example of such mixed languages is Tok Pisin, the official language of Papua New-Guinea, which originally arose as a Pidgin based on English and Austronesian languages; others are Kreyòl ayisyen, the French-based creole language spoken in Haiti, and Michif, a mixed language of Canada, based on the Native American language Cree and French.[120]
Linguistic diversity
SIL Ethnologue
defines a “living language” as “one that has at least one speaker for
whom it is their first language”. The exact number of known living
languages varies from 6,000 to 7,000, depending on the precision of
one’s definition of “language”, and in particular, on how one defines
the distinction between languages and dialects. As of 2016, Ethnologue cataloged 7,097 living human languages.[122] The Ethnologue establishes linguistic groups based on studies of mutual intelligibility, and therefore often includes more categories than more conservative classifications. For example, the Danish language that most scholars consider a single language with several dialects is classified as two distinct languages (Danish and Jutish) by the Ethnologue.[121]
According to the Ethnologue, 389 languages (nearly 6%) have
more than a million speakers. These languages together account for 94%
of the world’s population, whereas 94% of the world’s languages account
for the remaining 6% of the global population. To the right is a table
of the world’s 10 most spoken languages with population estimates from
the Ethnologue (2009 figures).[121]
Languages and dialects
There is no clear distinction between a language and a dialect, notwithstanding a famous aphorism attributed to linguist Max Weinreich that “a language is a dialect with an army and navy“.[123]
For example, national boundaries frequently override linguistic
difference in determining whether two linguistic varieties are languages
or dialects. Hakka, Cantonese and Mandarin are, for example, often classified as “dialects” of Chinese, even though they are more different from each other than Swedish is from Norwegian. Before the Yugoslav civil war, Serbo-Croatian was considered a single language with two dialects, but now Croatian and Serbian
are considered different languages and employ different writing
systems. In other words, the distinction may hinge on political
considerations as much as on cultural differences, distinctive writing systems, or degree of mutual intelligibility.[124]
Language families of the world
The world’s languages can be grouped into language families
consisting of languages that can be shown to have common ancestry.
Linguists recognize many hundreds of language families, although some of
them can possibly be grouped into larger units as more evidence becomes
available and in-depth studies are carried out. At present, there are
also dozens of language isolates: languages that cannot be shown to be related to any other languages in the world. Among them are Basque, spoken in Europe, Zuni of New Mexico, Purépecha of Mexico, Ainu of Japan, Burushaski of Pakistan, and many others.[125]
The language family of the world that has the most speakers is the Indo-European languages, spoken by 46% of the world’s population.[126] This family includes major world languages like English, Spanish, Russian, and Hindustani (Hindi/Urdu). The Indo-European family achieved prevalence first during the Eurasian Migration Period (c. 400–800 AD),[citation needed] and subsequently through the European colonial expansion, which brought the Indo-European languages to a politically and often numerically dominant position in the Americas and much of Africa. The Sino-Tibetan languages are spoken by 20%[126] of the world’s population and include many of the languages of East Asia, including Hakka, Mandarin Chinese, Cantonese, and hundreds of smaller languages.[127]
Africa is home to a large number of language families, the largest of which is the Niger-Congo language family, which includes such languages as Swahili, Shona, and Yoruba. Speakers of the Niger-Congo languages account for 6.9% of the world’s population.[126] A similar number of people speak the Afroasiatic languages, which include the populous Semitic languages such as Arabic, Hebrew language, and the languages of the Sahara region, such as the Berber languages and Hausa.[127]
The Austronesian languages are spoken by 5.5% of the world’s population and stretch from Madagascar to maritime Southeast Asia all the way to Oceania.[126] It includes such languages as Malagasy, Māori, Samoan, and many of the indigenous languages of Indonesia and Taiwan.
The Austronesian languages are considered to have originated in Taiwan
around 3000 BC and spread through the Oceanic region through
island-hopping, based on an advanced nautical technology. Other populous
language families are the Dravidian languages of South Asia (among them Kannada Tamil and Telugu), the Turkic languages of Central Asia (such as Turkish), the Austroasiatic (among them Khmer), and Tai–Kadai languages of Southeast Asia (including Thai).[127]
The areas of the world in which there is the greatest linguistic diversity, such as the Americas, Papua New Guinea, West Africa,
and South-Asia, contain hundreds of small language families. These
areas together account for the majority of the world’s languages, though
not the majority of speakers. In the Americas, some of the largest
language families include the Quechumaran, Arawak, and Tupi-Guarani families of South America, the Uto-Aztecan, Oto-Manguean, and Mayan of Mesoamerica, and the Na-Dene, Iroquoian, and Algonquian language families of North America. In Australia, most indigenous languages belong to the Pama-Nyungan family, whereas New Guinea is home to a large number of small families and isolates, as well as a number of Austronesian languages.[125]
Language endangerment
Together, the eight countries in red contain more than 50% of the
world’s languages. The areas in blue are the most linguistically diverse
in the world, and the locations of most of the world’s endangered
languages.
Language endangerment occurs when a language is at risk of falling out of use as its speakers die out or shift to speaking another language. Language loss occurs when the language has no more native speakers, and becomes a dead language. If eventually no one speaks the language at all, it becomes an extinct language.
While languages have always gone extinct throughout human history, they
have been disappearing at an accelerated rate in the 20th and 21st
centuries due to the processes of globalization and neo-colonialism, where the economically powerful languages dominate other languages.[128]
The more commonly spoken languages dominate the less commonly spoken
languages, so the less commonly spoken languages eventually disappear
from populations. The total number of languages in the world is not
known. Estimates vary depending on many factors. The consensus is that
there are between 6,000[129] and 7,000 languages spoken as of 2010, and that between 50–90% of those will have become extinct by the year 2100.[128] The top 20 languages,
those spoken by more than 50 million speakers each, are spoken by 50%
of the world’s population, whereas many of the other languages are
spoken by small communities, most of them with less than 10,000
speakers.[128]
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization
(UNESCO) operates with five levels of language endangerment: “safe”,
“vulnerable” (not spoken by children outside the home), “definitely
endangered” (not spoken by children), “severely endangered” (only spoken
by the oldest generations), and “critically endangered” (spoken by few
members of the oldest generation, often semi-speakers). Notwithstanding claims that the world would be better off if most adopted a single common lingua franca, such as English or Esperanto,
there is a consensus that the loss of languages harms the cultural
diversity of the world. It is a common belief, going back to the
biblical narrative of the tower of Babel in the Old Testament, that linguistic diversity causes political conflict,[28]
but this is contradicted by the fact that many of the world’s major
episodes of violence have taken place in situations with low linguistic
diversity, such as the Yugoslav and American Civil War, or the genocide of Rwanda, whereas many of the most stable political units have been highly multilingual.[130]
Many projects aim to prevent or slow this loss by revitalizing endangered languages and promoting education and literacy in minority languages. Across the world, many countries have enacted specific legislation to protect and stabilize the language of indigenous speech communities.
A minority of linguists have argued that language loss is a natural
process that should not be counteracted, and that documenting endangered
languages for posterity is sufficient.[131]
See also
Notes
The gorilla Koko reportedly uses as many as 1000 words in American Sign Language,
and understands 2000 words of spoken English. There are some doubts
about whether her use of signs is based on complex understanding or
simple conditioning; Candland (1993).
“Functional
grammar analyzes grammatical structure, as do formal and structural
grammar; but it also analyzes the entire communicative situation: the
purpose of the speech event, its participants, its discourse context.
Functionalists maintain that the communicative situation motivates,
constrains, explains, or otherwise determines grammatical structure, and
that a structural or formal approaches not merely limited to an
artificially restricted data base, but is inadequate even as a
structural account. Functional grammar, then, differs from formal and
structural grammar in that it purports not to model but to explain; and
the explanation is grounded in the communicative situation”; Nichols (1984)
The prefixed asterisk * conventionally indicates that the sentence is ungrammatical, i.e. syntactically incorrect.
Citations
Tomasello (1996)
Hauser, Chomsky & Fitch (2002)
“language”. The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (3rd ed.). Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company. 1992.
Lyons (1981:2)
Lyons (1981:1–8)
Trask (2007):129–31
Hauser & Fitch (2003)
Pinker (1994)
Saussure (1983)
Campbell (2001:96)
Chomsky (1957)
Trask (2007:93, 130)
Newmeyer (1998:3–6)
Evans & Levinson (2009)
Van Valin (2001)
Hockett, Charles F. The Problem of Universals in Language. 1966. Retrieved from “Archived copy”. Archived from the original on 10 November 2012. Retrieved 11 May 2013.
Hockett (1960); Deacon (1997)
Trask (1999):1–5
Engesser, Sabrina; Crane, Jodie S.; Savage, James L.; Russel, Andrew F.; Townsend, Simon W. (29 June 2015). “Experimental Evidence for Phonemic Contrasts in a Nonhuman Vocal System”. PLOS Biology. 13 (6): e1002171. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1002171. PMC 4488142  . PMID 26121619. Retrieved 18 August 2017.
. PMID 26121619. Retrieved 18 August 2017.
Engesser, Sabrina; Ridley, Amanda R.; Townsend, Simon W. (20 July 2017). “Element repetition rates encode functionally distinct information in pied babbler ‘clucks’ and ‘purrs‘“. Animal Cognition. 20 (5): 953–960. doi:10.1007/s10071-017-1114-6. PMID 28730513. Retrieved 18 August 2017.
Deacon (1997)
Trask (2007:165–66)
Haugen (1973)
Ulbaek (1998)
Tomasello (2008)
Anderson (2012:107)
Anderson (2012:104)
Clark,
Gary; Henneberg, Maciej (2017). “Ardipithecus ramidus and the evolution
of language and singing: An early origin for hominin vocal capability”.
HOMO. 68 (2): 101–121. doi:10.1016/j.jchb.2017.03.001. PMID 28363458.
Newmeyer (2005)
Trask (2007)
Campbell (2001:82–83)
Bloomfield 1914, p. 310
Clarke (1990):143–44
Foley (1997:82–83)
Croft & Cruse (2004:1–4)
Trask (1999:11–14, 105–13)
Fisher, Lai & Monaco (2003)
Lesser (1989:205–06)
Trask (1999:105–07)
Trask (1999:108)
Sandler & Lillo-Martin (2001:554)
MacMahon (1989:2)
MacMahon (1989:3)
International Phonetic Association (1999:3–8)
MacMahon (1989:11–15)
MacMahon (1989:6–11)
Ladefoged & Maddieson (1996)
Lyons (1981:17–24)
Trask (1999:35)
Lyons (1981:218–24)
Levinson (1983)
Goldsmith (1995)
International Phonetic Association (1999)
International Phonetic Association (1999:27)
Trask (2007:214)
International Phonetic Association (1999:4)
Stokoe, William C. (1960). Sign Language Structure: An Outline of the Visual Communication Systems of the American Deaf, Studies in linguistics: Occasional papers (No.  . Buffalo: Dept. of Anthropology and Linguistics, University of Buffalo.
. Buffalo: Dept. of Anthropology and Linguistics, University of Buffalo.
Stokoe, William C.; Dorothy C. Casterline; Carl G. Croneberg (1965). A dictionary of American sign languages on linguistic principles. Washington, D.C.: Gallaudet College Press
Sandler & Lillo-Martin (2001:539–40)
Trask (2007:326)
Coulmas (2002)
Trask (2007:123)
Lyons (1981:103)
Allerton (1989)
Payne (1997)
Trask (2007:208)
Trask (2007:305)
Senft (2008)
Aronoff & Fudeman (2011:1–2)
Bauer (2003); Haspelmath (2002)
Payne (1997:28–29)
Trask (2007:11)
Baker (2001:265)
Trask (2007:179)
Trask (2007:218–19)
Nichols (1992);Comrie (1989)
Croft (2001:340)
Greenberg (1966)
Comrie (2009:45); MacMahon (1994:156)
Croft (2001:355)
“Wall of Love – Mur des Je t’aime – Montmartre”. Travel France Online. Retrieved 30 November 2014.
Campbell (2004)
Austin & Sallabank (2011)
Levinson (1983:54–96)
Levinson (1983:226–78)
Levinson (1983:100–69)
Bonvillian,
John D.; Michael D. Orlansky; Leslie Lazin Novack (December 1983).
“Developmental milestones: Sign language acquisition and motor
development”. Child Development. 54 (6): 1435–45. doi:10.2307/1129806. PMID 6661942.
O’Grady, William; Cho, Sook Whan (2001). “First language acquisition”. Contemporary Linguistics: An Introduction (fourth ed.). Boston: Bedford St. Martin’s.
Kennison (2013)
“First Impressions: We start to pick up words, food preferences and hand-eye coordination long before being born”, Scientific American, vol. 313, no. 1 (July 2015), p. 24.
Beth Skwarecki, “Babies Learn to Recognize Words in the Womb”, Science, 26 August 2013 [1]
Macaro, Ernesto, ed. (2010). Continuum companion to second language acquisition. London: Continuum. pp. 137–57. ISBN 978-1-4411-9922-5.
Duranti (2003)
Foley (1997)
Agha (2006)
Dixon (1972:32–34)
Foley (1997:311–28)
Olson (1996)
Aitchison (2001); Trask (1999:70)
Clackson (2007:27–33)
Aitchison (2001:112)
Zentella (2002:178)
Labov (1994)
Labov (2001)
Thomason (2001:1)
Romaine (2001:513)
Campbell (2002)
Aikhenvald (2001)
Thomason & Kaufman (1988); Thomason (2001); Matras & Bakker (2003)
Lewis (2009)
“Ethnologue statistics”. Summary by world area | Ethnologue. SIL.
Rickerson, E.M. “What’s the difference between dialect and language?”. The Five Minute Linguist. College of Charleston. Archived from the original on 19 December 2010. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
Lyons (1981:26)
Katzner (1999)
Lewis (2009), “Summary by language family“
Comrie (2009); Brown & Ogilvie (2008)
Austin & Sallabank (2011)
Moseley (2010): “Statistics“
Austin & Sallabank (2011:10–11)
Works cited
- Agha, Agha (2006). Language and Social Relations. Cambridge University Press.
- Aikhenvald, Alexandra (2001). “Introduction”. In Alexandra Y. Aikhenvald; R. M. W. Dixon. Areal diffusion and genetic inheritance: problems in comparative linguistics. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 1–26.
- Aitchison, Jean (2001). Language Change: Progress or Decay? (3rd (1st edition 1981) ed.). Cambridge, New York, Melbourne: Cambridge University Press.
- Allerton, D. J. (1989). “Language as Form and Pattern: Grammar and its Categories”. In Collinge, N.E. An Encyclopedia of Language. London:NewYork: Routledge.
- Anderson, Stephen (2012). Languages: A Very Short Introduction. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-959059-9.
- Aronoff, Mark; Fudeman, Kirsten (2011). What is Morphology. John Wiley & Sons.
- Austin, Peter K; Sallabank, Julia (2011). “Introduction”. In Austin, Peter K; Sallabank, Julia. Cambridge Handbook of Endangered Languages. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-88215-6.
- Baker, Mark C. (2001). “Syntax”. In Mark Aronoff; Janie Rees-Miller. The Handbook of Linguistics. Blackwell. pp. 265–95.
- Bauer, Laurie (2003). Introducing linguistic morphology (2nd ed.). Washington, D.C.: Georgetown University Press. ISBN 0-87840-343-4.
- Bett, R. (2010). “Plato and his Predecessors”. In Alex Barber & Robert J Stainton (eds.). Concise Encyclopedia of Philosophy of Language and Linguistics. Elsevier. pp. 569–70.
- Bloomfield, Leonard (1914). An introduction to the study of language. New York: Henry Holt and Company.
- Brown, Keith; Ogilvie, Sarah, eds. (2008). Concise Encyclopedia of Languages of the World. Elsevier Science. ISBN 0-08-087774-5.
- Clackson, James (2007). Indo-European Linguistics: An Introduction. Cambridge University press.
- Campbell, Lyle (2002). “Areal linguistics”. In Bernard Comrie, Neil J. Smelser and Paul B. Balte. International Encyclopedia of Social and Behavioral Sciences. Oxford: Pergamon. pp. 729–33.
- Campbell, Lyle (2004). Historical Linguistics: an Introduction (2nd ed.). Edinburgh and Cambridge, MA: Edinburgh University Press and MIT Press.
- Campbell, Lyle (2001). “The History of Linguistics”. In Mark Aronoff; Janie Rees-Miller. The Handbook of Linguistics. Blackwell. pp. 81–105.
- Candland, Douglas Keith (1993). Feral Children and Clever Animals: Reflections on Human Nature. Oxford University Press US. pp. 293–301. ISBN 0-19-510284-3.
- Chomsky, Noam (1957). Syntactic Structures. The Hague: Mouton.
- Chomsky, Noam (2000). The Architecture of Language. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Clarke, David S. (1990). Sources of semiotic: readings with commentary from antiquity to the present. Carbondale: Southern Illinois University Press.
- Comrie, Bernard (1989). Language universals and linguistic typology: Syntax and morphology (2nd ed.). Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 0-226-11433-3.
- Comrie, Bernard, ed. (2009). The World’s Major Languages. New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-35339-7.
- Coulmas, Florian (2002). Writing Systems: An Introduction to Their Linguistic Analysis. Cambridge University Press.
- Croft, William; Cruse, D. Alan (2004). Cognitive Linguistics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Croft, William (2001). “Typology”. In Mark Aronoff; Janie Rees-Miller. The Handbook of Linguistics. Blackwell. pp. 81–105.
- Crystal, David (1997). The Cambridge Encyclopedia of Language. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Cysouw, Michael; Good, Jeff (2013). “Languoid, doculect and glossonym: Formalizing the notion ‘language‘“. Language Documentation and Conservation. 7: 331–59.
- Deacon, Terrence (1997). The Symbolic Species: The Co-evolution of Language and the Brain. New York: W.W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-393-31754-1.
- Devitt, Michael; Sterelny, Kim (1999). Language and Reality: An Introduction to the Philosophy of Language. Boston: MIT Press.
- Dixon, Robert M. W. (1972). The Dyirbal Language of North Queensland. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-08510-1.
- Duranti, Alessandro (2003). “Language as Culture in U.S. Anthropology: Three Paradigms”. Current Anthropology. 44 (3): 323–48. doi:10.1086/368118.
- Evans, Nicholas; Levinson, Stephen C. (2009). “The myth of language universals: Language diversity and its importance for cognitive science”. Behavioral and Brain Sciences. 32 (5): 429–92. doi:10.1017/s0140525×0999094x.
- “First Impressions: We start to pick up words, food preferences and hand-eye coordination long before being born”, Scientific American, vol. 313, no. 1 (July 2015), p. 24.
- Fisher,
Simon E.; Lai, Cecilia S.L.; Monaco, Anthony P. (2003). “Deciphering
the Genetic Basis of Speech and Language Disorders”. Annual Review of Neuroscience. 26: 57–80. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.26.041002.131144. PMID 12524432.
- Fitch, W. Tecumseh (2010). The Evolution of Language. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Foley, William A. (1997). Anthropological Linguistics: An Introduction. Blackwell.
- Goldsmith, John A (1995). “Phonological Theory”. In John A. Goldsmith. The Handbook of Phonological Theory. Blackwell Handbooks in Linguistics. Blackwell Publishers. ISBN 1-4051-5768-2.
- Greenberg, Joseph (1966). Language Universals: With Special Reference to Feature Hierarchies. The Hague: Mouton & Co.
- Haspelmath, Martin (2002). Understanding morphology. London: Arnold, Oxford University Press. (pbk)
- Haugen, Einar (1973). “The Curse of Babel”. Daedalus. 102 (3, Language as a Human Problem): 47–57.
- Hauser,
Marc D.; Chomsky, Noam; Fitch, W. Tecumseh (2002). “The Faculty of
Language: What Is It, Who Has It, and How Did It Evolve?”. Science. 298 (5598): 1569–79. doi:10.1126/science.298.5598.1569. PMID 12446899.
- Hauser, Marc D.; Fitch, W. Tecumseh (2003). “What are the uniquely human components of the language faculty?”. In M.H. Christiansen and S. Kirby. Language Evolution: The States of the Art (PDF). Oxford University Press. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 August 2014.
- Hockett, Charles F. (1960). “Logical considerations in the study of animal communication”. In W.E. Lanyon; W.N. Tavolga. Animals sounds and animal communication. pp. 392–430.
- International Phonetic Association (1999). Handbook of the International Phonetic Association: A guide to the use of the International Phonetic Alphabet. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-65236-7.
- Katzner, Kenneth (1999). The Languages of the World. New York: Routledge.
- Kennison, Shelia (2013). Introduction to Language Development. SAGE.
- Labov, William (1994). Principles of Linguistic Change vol.I Internal Factors. Blackwell.
- Labov, William (2001). Principles of Linguistic Change vol.II Social Factors. Blackwell.
- Ladefoged, Peter (1992). “Another view of endangered languages”. Language. 68 (4): 809–11. doi:10.1353/lan.1992.0013.
- Ladefoged, Peter; Maddieson, Ian (1996). The sounds of the world’s languages. Oxford: Blackwell. pp. 329–30. ISBN 0-631-19815-6.
- Lesser, Ruth (1989). “Language in the Brain: Neurolinguistics”. In Collinge, N.E. An Encyclopedia of Language. London:NewYork: Routledge.
- Levinson, Stephen C. (1983). Pragmatics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Lewis, M. Paul (ed.) (2009). “Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Sixteenth edition”. Dallas, Tex.: SIL International.
- Lyons, John (1981). Language and Linguistics. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-29775-3.
- Macaro, Ernesto, ed. (2010). Continuum companion to second language acquisition. London: Continuum. pp. 137–57. ISBN 978-1-4411-9922-5.
- MacMahon, April M.S. (1994). Understanding Language Change. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-44119-6.
- MacMahon, M.K.C. (1989). “Language as available sound:Phonetics”. In Collinge, N.E. An Encyclopedia of Language. London:NewYork: Routledge.
- Matras, Yaron; Bakker, Peter, eds. (2003). The Mixed Language Debate: Theoretical and Empirical Advances. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 3-11-017776-5.
- Moseley, Christopher, ed. (2010). Atlas of the World’s Languages in Danger, 3rd edition. Paris: UNESCO Publishing.
- Nerlich, B. (2010). “History of pragmatics”. In L. Cummings. The Pragmatics Encyclopedia. London/New York: Routledge. pp. 192–93.
- Newmeyer, Frederick J. (2005). The History of Linguistics. Linguistic Society of America. ISBN 0-415-11553-1.
- Newmeyer, Frederick J. (1998). Language Form and Language Function (PDF). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Nichols, Johanna (1992). Linguistic diversity in space and time. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 0-226-58057-1.
- Nichols, Johanna (1984). “Functional Theories of Grammar”. Annual Review of Anthropology. 13: 97–117. doi:10.1146/annurev.an.13.100184.000525.
- Olson, David R. (1996). “Language and Literacy: what writing does to Language and Mind”. Annual Review of Applied Linguistics. 16: 3–13. doi:10.1017/S0267190500001392.
- Payne, Thomas Edward (1997). Describing morphosyntax: a guide for field linguists. Cambridge University Press. pp. 238–41. ISBN 978-0-521-58805-8.
- Pinker, Steven (1994). The Language Instinct: How the Mind Creates Language. Perennial.
- Romaine, Suzanne (2001). “Multilingualism”. In Mark Aronoff; Janie Rees-Miller. The Handbook of Linguistics. Blackwell. pp. 512–33.
- Saussure, Ferdinand de (1983) [1913]. Bally, Charles; Sechehaye, Albert, eds. Course in General Linguistics. Translated by Roy Harris. La Salle, Illinois: Open Court. ISBN 0-8126-9023-0.
- Sandler, Wendy; Lillo-Martin, Diane (2001). “Natural Sign Languages”. In Mark Aronoff; Janie Rees-Miller. The Handbook of Linguistics. Blackwell. pp. 533–63.
- Senft, Gunter, ed. (2008). Systems of Nominal Classification. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-06523-8.
- Swadesh, Morris (1934). “The phonemic principle”. Language. 10 (2): 117–29. doi:10.2307/409603. JSTOR 409603.
- Tomasello, Michael (1996). “The Cultural Roots of Language”. In B. Velichkovsky and D. Rumbaugh. Communicating Meaning: The Evolution and Development of Language. Psychology Press. pp. 275–308. ISBN 978-0-8058-2118-5.
- Tomasello, Michael (2008). Origin of Human Communication. MIT Press.
- Thomason, Sarah G.; Kaufman, Terrence (1988). Language Contact, Creolization and Genetic Linguistics. University of California Press.
- Thomason, Sarah G. (2001). Language Contact – An Introduction. Edinburgh University Press.
- Trask, Robert Lawrence (1999). Language: The Basics (2nd ed.). Psychology Press.
- Trask, Robert Lawrence (2007). Stockwell, Peter, ed. Language and Linguistics: The Key Concepts (2nd ed.). Routledge.
- Ulbaek, Ib (1998). “The Origin of Language and Cognition”. In J. R. Hurford & C. Knight. Approaches to the evolution of language. Cambridge University Press. pp. 30–43.
- Van Valin, jr, Robert D. (2001). “Functional Linguistics”. In Mark Aronoff; Janie Rees-Miller. The Handbook of Linguistics. Blackwell. pp. 319–37.
- Zentella, Ana Celia (2002). “Spanish in New York”. In García, Ofelia; Fishman, Joshua. The Multilingual Apple: Languages in New York City. Walter de Gruyter.
External links
This audio file was created from a revision of the article “Language” dated 2005-07-19, and does not reflect subsequent edits to the article. (Audio help)
| [show]
Links to related articles
|
Languages
Leave a Reply