Posted by: site admin @ 1:17 am

 pools as possible in entire Karnataka.
pools as possible in entire Karnataka. |
Verse 45. The Seeker Understands
Explanation: In the previous stanza the question was raised |
 |
Verse 46. Who Conquers Death?
Explanation: This body of ours is like froth, bubbles, or |
 |
Verse 47. Pleasure Seeker Is Swept Away
Explanation: Those men and women , fascinated by worldly things, |
 |
Verse 48. Attachment To Senses If Folly
Explanation: Those who pursue worldly pleasures are like garland-makers |
 |
Verse 49. The Monk In The Village
Explanation: The bee extracts honey from flowers without |
 |
Verse 50. Look Inwards And Not At Others
Explanation: Do not find fault with others. Do not worry about |
 |
Verse 51. Good Words Attract Only Those Who Practice
Explanation: A flower may be quite attractive, alluring. It |
 |
Verse 52. Good Words Profit Only Those Who Practise
Explanation: A flower may be quite attractive, alluring and |
 |
Verse 53. Those Born Into This World Must Acquire Much Merit
Explanation: The deft maker of garlands takes a variety of |
 |
Verse 54. Fragrance of Virtue Spreads Everywhere
Explanation: The world knows, many a sweet smelling flower |
 |
Verse 55. Fragrance Of Virtue Is The Sweetest Smell
Explanation: Sandalwood, lavender, water-lily and the jasmine |
 |
Verse 56. Fragrance Of Virtue Wafts To Heaven
Explanation: The fragrance of lavender and sandalwood is quite |
 |
Verse 57. Death Cannot Trace The Path Of Arahats
Explanation: Of those noble one, who are perfect in behaviour, |
 |
Verse 58. Lotus Is Attractive Though In A Garbage Heap
Explanation: Someone is likely to dump refuse on a high road. |
 |
Verse 59. Arahats Shine Wherever They Are
Explanation: In the same way, in the heap of rubbish made |
 |
Verse 44. The Garland-Maker
Explanation: An expert in garland making will select, pluck |
video is about dream vision of J Chandrasekharan who has constructed
Kushinara Nibbana Bhumi Pagoda Bengaluru, This pagodan is built where
people can come make use of the place and get maximum benefit.

 Bell Peppers
Bell Peppers Cucumber
Cucumber  Carrots
Carrots  Beans in pots like Free Birds
Beans in pots like Free Birds  in Vegan
in Vegan  White Home to make the hungry minds to glow like Lotus.
White Home to make the hungry minds to glow like Lotus.Aboriginal Awakened Societies Thunder ” Hum Prapanch Prabuddha
Prapanchmay karunge.” (We will make the whole world Prabuddha Prapanch
at $62.00 which plays a role in generating energy in the human body
available ‘for the price of a coffee a day’ a Stunning anti-ageing
breakthrough could see humans live to 150 years and regenerate organ.New
process has been found by Harvard Professor David Sinclair and
researchers from the University of New South Wales, involving cell
reprogramming.
to the University of Singapore survey/review based on 131 countries.
From June 18, world will be 100% free and happy from December 8th. Their
predictions about Italy and Spain fit exactly.
of COVID Tests Says Pandemic is Biggest Hoax Ever Perpetrated It is
like a blind man searching for a black cat in a dark room which is not
there.
video is about dream vision of chandrashaker who has build terrace
vipassana pagoda in Bangalore,new thippasandra, This pagodan is built
where people ca…
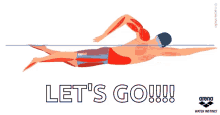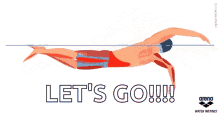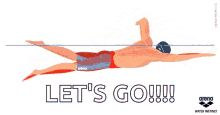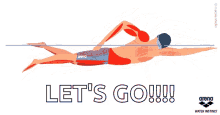
often devolves into autopilot behavior in which you focus only on
getting in the distance you’ve planned, or ‘following the black line.’
This is a lost opportunity.
can also be an immensely rewarding opportunity to practice mindfulness.
By swimming mindfully, we can transform routine lap sessions into an
immersive form of moving meditation.” — Terry Laughlin, founder of Total
Immersion Swimming.
you begin swimming, focus on each stroke. Notice the feeling of the
wetness on your skin. Feel yourself — buoyant — moving through water.
on your breath. As you take breaths, shift your focus from a stroke
rhythm to a breathing rhythm, noticing the unbroken alternation of
in-breaths and out-breaths.
head and spine. Visualize being towed forward by a line attached to the
top of your head, so your head and spine are both lengthening and
always moving in the direction you want to travel.
you continue with your strokes, focus on the feeling of your arms
entering and leaving the water. Feel the cool, dry air on your arms
briefly; then the wet thickness of the water for a longer period of
submersion.
serving in Iraq for 3 years, swimming was the only way I could relax
when I came back. The requirement to breathe brought oxygen back into my
brain, which was still in a constant state of hypervigilance. The
coolness of the water replenished my parched body. The blue color of the
water dazzled my eyes after seeing nothing but brown. And the rhythmic
motion and quiet splashing gently brought peace and calm into my body.
Pure healing.-SEB
you want to swim well, you are always thinking about breath, stroke,
alignment, etc. Ask anyone, coach or swimmer, in a master’s swim
program. Or anyone in any formal swim program for that matter. BTW, the
black line, interval, pace, completing the set, minding the time clock,
all require mindfulness.
anything you want to do well required mindfulness. For example, if you
play a musical instrument, you have to be mindful of (pay attention to)
intonation, timing, dynamics, etc.
Murcia Spain we swim.for meditation and against the clock .teacher is a
backstroke medalist yoga expert.we sing outloud while doing 3K or
silently…Rockefeller once said. ” he who dies having done the most laps
wins. “.-murcia.es

recommend swimming as one of the best exercises around, and for good
reason. When we swim, the main muscle groups all go to work in a way
that doesn’t put undue stress on the body. This makes it a wholesome
aerobic exercise for young and old alike. The health benefits of this
kind of workout include:
people enjoy swimming because it’s so refreshing and good for you. But
you could go the extra lap and practice mindful swimming – and get the
best of both worlds. With mindful swimming, instead of just focusing on
reaching a certain goal, you pay full attention to the exercise and the
sensations experienced as you swim. Extending your mindfulness practice
into swimming is a great way to break up the routine of sitting
meditation.
answer depends on the swimmer! Meditation is about awareness, and it
might be argued that awareness is possible in every situation, including
swimming. With mindful swimming, you can enjoy the current moment
without worrying about any stressful issues at work, home or elsewhere.
of mindlessly plunging into the water and doing your laps, take a few
moments to formulate the intention of being entirely present in the
water. Once you’ve begun swimming, see if you can maintain awareness of
the here and now. Enjoy the feeling of buoyancy as you glide across the
pool and take note of other physical sensations – wetness, scent, sound,
etc. Remain present as your arms enter and leave the water, your legs
propel your body forward and your head follows the rhythm of the
movement. How does it feel? Acknowledging sensations that you don’t
usually notice is part of what makes swimming as meditation so
enjoyable. Alternatively, when swimming laps or floating, you may also
choose to focus on your breath.
you meditate, the mind is no longer bound by the anxieties and stresses
that usually take up so much mental space. Instead, the mind is
spacious and refreshed, and you feel rejuvenated. This naturally
inspires you to work on bettering yourself and improving the lives of
others. By incorporating the exercise of swimming as meditation into
your mindfulness regime, you train in extending your “on-the-cushion”
practice into your everyday life.
swimmers tend to repeat the same movements every time they train. It’s
easy for them to give their minds free rein to wander as they swim
instead of being mindfully aware of their breath and physical
sensations. In her article “Mindful Swimming” in Swimming World
Magazine, former competitive swimmer Tonya Nascimento believes that
mindfulness can help athletes while training as well as while competing.
“At all levels, swim meets can have a multitude of distractions that
capture your mind and direct your attention away from your races. [ …]
The goal of mindfulness is to develop a sense of calm in the midst of
the storm; it is to gain control over one’s own thoughts. By becoming
aware of your thoughts, you can decide to let go of those thoughts that
hinder your performance, and decide to concentrate on only those
thoughts that help you improve,” she writes.
number of national swimming teams (including the U.S. Olympic team)
have incorporated mindfulness in their training sessions. The feedback
has been positive: athletes have reported improved performances when
they focus on being fully present rather than focusing on the goal
(winning!) alone. Mindful presence helps swimmers maintain balance, and
balance fosters peak performance.
trying mindful swimming, make sure your swimming level is good enough.
Once you get the groove of it, you’ll realize that swimming and
meditation are an awesome match. Most importantly, remember that
swimming – and meditating – should be enjoyable!
reading this article it’s clear that you’re interested in the practice
of meditation and its results: experiencing genuine joy and well-being.
You’ve come to the right place. Mindworks is a non-profit with a mission
to share the most authentic and proven meditation guidance to you and
our worldwide community.
meditation practice develops the most fundamental axis of our being,
it’s essential to rely on clear, progressive and genuine meditation
methods from authentic guides. In order to fully transmit to you the
full potential of genuine meditation, we created the 9-level Mindworks
Journey to Well-Being.
so sure you’ll benefit we now offer you Mindworks Journey Level 1:
Meditation Fundamentals course for Free. Click the link below to learn
more.
recommend swimming as one of the best exercises around, and for good
reason. When we swim, the main muscle groups all go to work in a way
that doesn’t put undue stress on the body. This makes it a wholesome
aerobic exercise for young and old alike. The health benefits of this
kind of
WORLD WILL BE FREE FROM HOAX - STRENGTHENING THE TRUST FOR BEST OF HEALTH -SINGAPORE UNIVERSITY SURVEY
Dhammarakkhita

The Yoga Sutras of Patanjali: a manual of Buddhist meditation?
Translation
and free adaptation of the article published on the blog “Theravadin -
Theravada Practice Blog” (http://theravadin.wordpress.
summary, this comparison is quite obvious that the author of Yoga Sutra was highly influenced by Buddhist philosophy and meditation practice, possibly contemporaneously to the author.
proximity of the Yoga Sutra-style, vocabulary, and subject to canonical
texts in Pali could also mean simply that Patanjali - or whoever it is
that inspired his writings - had practiced meditation from a Buddhist
contemplative community, a community of monks for a time before
returning to Brahmanism and then the movement would have rephrased his
experience in order to add a divine touch to your experience, making
substantial use of technical terms of Buddhist meditation, as originally
framed or developed by the Buddha for the purpose of contemplative
practice. But this would be pure speculation, because there is so far no studies or historical finding that supports this understanding.
is also possible, even likely, that the Buddhist meditation had so
broadly permeated the practice Hindu / Brahman at the time (after years
of a strong cultural influence began with Buddhist proselytism promoted
by Ashoka the Buddhist Sangha in his reign and Consolidation of India),
that these technical terms as well as descriptions of practice of jhana /
dhyana (meditative absorptions) have it built into common knowledge at
the point of no longer sounding particularly Buddhists. Something
similar to what happens today with the adoption of the ideas of
“nirvana” and “karma” in Western culture, in Christian countries.
particular, if the Yoga Sutra is read in one continuous line is amazing
how close the text is the thoughts and topics about samadhi, jhana
meditation and Samatha (concentration) as defined in the ancient texts
in Pali Buddhist.
at the “Ashtanga Yoga” or the “Eightfold Path of Yoga” (sic) we are
certainly inclined to think the definition of the central Buddha of the
Noble Eightfold Path.
instead of following the Buddhist literary definition of the Noble
Eightfold Path, the interpretation of the eightfold path of yoga follows
(to our surprise?) Another description of the Buddhist path: the one
given by the Buddha as he described how he taught his disciples to
practice in your system meditative, which consists of a number of steps
outlined in various suttas of the volume of speeches with Mean Length
(as in Ariyapariyesana Sutta, MN 26, etc.) and remind us much of the way
“yogic” (pragmatic?), as devised by Patanjali at Yoga Sutra
far as terminology goes aa long in the Yoga Sutra that reminds us of
formulations of the Buddhist Pali Canon and even more Abhidharma
Sarvastivada Sautrantika and school. “Robert Thurman writes that
Patanjali was influenced by the success of the Buddhist monastic system
to formulate its own matrix for the version of thought he considered
orthodox (…) The division between Eight States (Sanskrit Ashtanga)
Yoga is reminiscent of the Noble Eightfold Path of Buddha, and the
inclusion of brahmavihara (Yoga Sutra 1:33) also shows the influence of
Buddhism in parts of the Sutras. “
this is where the subject becomes interesting for us here on this blog
and its relevance to the practice of Buddhist meditation.
all the above tells us that the Yoga Sutra is a comment Hindu / Brahmin
or at least a photograph of meditation practices common (influenced by
Buddhism) in the second century BC?
this is because the text is not a Buddhist but shares a “core” of
fundamental ideas on meditation to be able to take it as a sign pointing
to a deeper understanding of some of the terminology in the context of
the first centuries of Buddhist practice.
if the Yoga Sutra is read in a Buddhist context, one can have some idea
of how people understood at that time and (ou!) practiced Buddhist
meditation? Could this be of some help in triangular or point of which was the direction of former Buddhist meditation?
more we know how people practiced a few centuries after the Buddha’s
Parinibbana, the more we can understand how some of his teachings have
evolved and how they were implemented and explained / taught.
makes this fascinating idea is that this text would definitely be
filterable through the eyes of a Hindu / Brahman, but he is still
influenced by the “knowledge” of Buddhist meditation apparently so well
received, and the time of his writing had become the mainstream
“contemplative practices. This
would show us how and in what particular point, was considered to be
the “essence” of meditation (in addition to being philosophical
discussion of its purpose) in order to be considered universally true,
then that can be “merged” into other forms of practice religious.
they were considered “truth” and “accepted” so that the author Hindu /
Brahman had no other choice but to incorporate them into their theistic
philosophy, reminding us Western Christians today that due to the common
acceptance of the idea karma / kamma, sometimes find ways to
incorporate this idea in their religious views.
(ignorance), Asmita (egoism), raga-Dvesha (desires and aversions),
Abhinivesha (clinging to mundane life) are the five klesha or distress. Destroy these afflictions [e] You will realize Samadhi. “
[Free translation of the original quote from Wikipedia]
impresses the reader as Buddhist before this paragraph is the simple
fact that all these impurities listed are those that no longer are you
supposed to Arahant one, or Awakened (!!!). That is, according to the text of Patanjali, the “Samadhi of Conduct” would be conceptually the same as the Buddhist Liberation.
ignorance or mental turvidão is even mentioned in the first place,
while clearly a Buddhist point of view is considered the root of all
problems.
“asmita”, which is superficially translated as “selfishness” by
understanding that had developed in shallow Sanskrit tradition that was
ignorant of the deeper meaning of that term as used in the suttas of the
Pali Canon (or tried to distort to suit your context religious).
term Buddhist in particular, pointing to the deeply embedded “notion
that it is” (ASMI-tā) has a clear explanation in the suttas, but here in
this passage and elsewhere, is reduced to a mere “selfishness” as a
moral impurity devoid of its original psychological application. In
the suttas “ASMI-Mana” is a deeply rooted psychological tendency that
only a Arahant (Iluminsfo) won [see post “The scent of am” blog
Theravadin].
there is also “abhinivesa”, a term the Buddha uses to explain how our
mind comes in and assumes the five groups of attachment. The
term “Nives” denotes a dwelling, a house - a simile brought by the
Buddha to show how our consciousness moves “inside” of the contact
experience of the senses and settles as if living in a house (see Sutta
Nipata, Atthakavagga , and Haliddakani Magandiya Sutta Sutta). This
usage is decreased very particular psychological context in Hindu /
Brahmin to denote only an “attachment to worldly life.”But here is worth
questioning whether this was also shared by superficial understanding
or just by Patanjali Yoga Sutra later commentators, who have lost sight
of these implications for not having knowledge of or access to the
preceding context of Buddhism in the Yoga Sutra was written?
have another pearl of a Buddhist point of view, which can be considered
truly revealing: the use of the word “Dharana” in the text of
Patanjali
term “Dharana”, which literally means short and “I can hold, carry,
keep (in mind)” is a good description of the task faced in Buddhist
contemplative practice, regardless of what tradition / school
considered.
meaning of the Buddhist term “sati” (which means reminder / recall) and
what is general and now translated simply as “mindfulness” - a
translation that often aboard with questions.And the reason is as follows, in summary: To maintain the object of meditation in mind you need to remember it. Remember here that means you have to hold, keep in mind, your object of concentration. This s exactly what makes the faculty of memory, usually being pushed away by the impressions with new information by the six senses, which, if penetrated, would result in more or less a wild spin.If you are able to sustain their concentration on one point however - or even as much as you can keep it, one of the laws of functioning of themind that the Buddha rediscovered and explained in detail that this ebate is “artificial” senses the support and focus on a particular mental object equivalent to a minor sensory stimulus. As a result of mental calmness and happiness (piti) and happiness index (sukha) will arise and show signs of the primeirs a stronger concentration - these being two of the five factors of meditative absorption (jhana), along with (i) directed thought (vitakka) (ii) sustained (Vicara) and (iii) equanimity (Upekkha). This is also the reason why is quite logical that samma sati, mindfulness, has to come before samma samadhi, full concentration in the Noble Eightfold Path of Buddhism - or, as shown in this case in the Yoga Sutra, “Dharana” would be the stage immediately prior to “Delivering the Samadhi.” In this case the Yoga Sutra throws much light on the original meaning as understood in the early centuries of Buddhist practice and can help u reach a more precise understanding of what “samma sati, right mindfulness, originally meant or pointed. (In Theravadin blog post is a rather plain and that shows how sati yoniso manasikara are coming in practical terms, check this link ). On the opposite side, or better, understanding it as a byproduct of the
practice of sati is no other term that would best be described as mindfulness.” The Pali term is sampajaññā - which literally means “next-consideration”, eg, be well aware of when performing an action, then a “clear understanding” of what it does - but this activity is a result of sati, as having the mind fixed on an object leads to a refined consciousness that arises when during the next\ and keep the mind of an object, creating a clear understanding of the ew sensory impressions that may enter. According to this concept, mindfulness would be a result of sati and not the practice of sati in itself! But again, both activities are happening almost simultaneously, even if not in the same order and then the current use of the term translated can be done - at the same time a fine distinction, however, has its benefits. You can not keep an object from the standpoint of mind without which would create or develop mindfulness in mind - but (unfortunately!) you may be aware of all your actions that you work without the right concentration - as when eat an ice cream, in seeking the sensual pleasure, an example of mproper care. This being the fact that unfortunately idealize the interpretations of some Westerners who want to say “Buddhist”. There is a difference between deliberately let himself be led by sense mpressions by focusing on their physical pleasures and enhancing / supporting raga (desire) and nandi (joy) - and, from the perspective of Gotama Buddha, put his feet on the ground using the mindful memory and thus experiencing a more refined awareness of trying to get it off the shaft so that it results in a greater mindfulness, in the culmination of this experience flows into total equanimity in the face of both pleasurable and painful sensations. Thus, then, we must understand as vipassanā is no way a synonym mindfulness (sati) but something that springs from the combination of all these factors especially the last two, samma sati (mindfulness) and samma samadhi (right concentration) applied to the relentless observation of what appears to be in front of (yathabhuta). You could say, vipassanā is a name for the Buddhist practice of sati associated samadhi directed to the view anicca / anatta / dukkha (ie, generating the wisdom of the vision of these three features) in the processes of the six senses, including any mental activity. Thus, one will find the term vipassanā but the idea of sati in the Yoga Sutra, Buddhist texts mention as the first term clearly having samādhi as just the beginning of the journey to insight and access for example aniccanupassana . Finish here the parenthesis. Suffice to say that any particular reference to the Buddhist philosophy citing anicca antta or point to the goal of Nibbana, a philosophical proposition to which the system of Yoga certainly does not refer.In essence the school of Yoga can be placed below the postures eternalists. So while it definitely does need to produce sati-samadhi, definitely does not need to understand is samadhi anicca, dukkha and anatta - that does not sound very compatible with the worldview of a eternalistic. Before this, all spiritual approach arise due to the attempt to interpret Samadhi Yoga Sutra as marriage or at least as close as you can get from a “God”, a “Lord.” Something hat sounds quite natural in the end to a theist - such as an Evangelical Christian would never interpret the reduction of its focus on mental object unique sensual ecstasy and consequently a mere effect of a psychological technique, but he would label it “the divine sign of God touching him. “ It is for this reason that, according to the Buddha Dhamma, in fact in most situations we are inclined to be led by the plots of our senses, including the mental impressions / thoughts / feelings / perceptions - and therefore tend to limit ourselves to go beyond such experiences also distorted the merger would allow access to insight and liberation. Returning o the context of comparison with the Christian interpretation of this ecstasy, in short what Patanjali is facing such a theistic interpretation sounds like someone moving a large portion of vocabulary and terminology for the New Testament, which gives this ring a Buddhist. The unny thing is that this is exactly how many of the contemporary New Age books are written - an amalgam of the terms of Western Spirituality Christian trying to express a view east. So one can imagine that the situation in India was similar to that when the Yoga Sutra was written addressing the Buddhist philosophy of that era.The remaining Buddhist philosophy with his particular terminology established by the Buddha himself would have become so pervasive in religious thought, so to make seemingly trusted what was written on meditation was a need to borrow or rely on several of these Buddhist concepts predominant. This had largely been done or even conscious, as most New Age authors present not even reflect the content of their texts but about the message you want to spend. Thus, below is done in a way a translation - or rather a translation of a ransliteration given the proximity between languages - as was done with the text of the Yoga Sutra in Sanskrit brought back to Pāli. Similar to what has been done this Sutra ( Theravadin available on the blog, in English on this link ) the exercise helps us see how the same text would sound the Pāli language, opening then find parallels in ancient Buddhist texts, the suttas. However, having said all that, pragmatism invoked by the text (which is what makes it so valuable) also indicates much more than a simple textual exploration. As you read this you can not discern the notion, especially since the position of a meditator concentration of whoever has written or inspired by this text, at some point personally experienced jhana and samadhi and wanted to convey his experience making use a rich language Buddhist meditatio on the same interpretation being directed to an audience Brahman / proto-Hindu India 200 BC. Anyway, check by itself - the pauses between sets of paragraphs labeled in bold are the author / translator and some important technical terms Buddhists were deployed, with additional comments made in italics:
- Patañjalino yogasuttaṃ (Part I of IV)
- Introduction
- tha yogānusāsanaṃ | | 1 |
- And now a statement about the European Union (Yoga
- [1] Read yourself to be the object of meditation, or an instruction (anusāsana) on the med yogo-citta-vatta nirodho | | 2 | | The Union (Yogo) is the extinction of the movement of the min [2] in this passage denotes vatta turbulence, swirl, activity - literally wandering, circling, confused. In this context broadly means “meditation is (…) a stop to the busy mind,” which is very active and its activity suggests a walk in circles. Probably the most direct (and correct) translati Tada ditthi (muni) svarūpe’avaṭṭhānaṃ | | 3 | | (Only) then he who sees is allowed (to be) in (his) true nature.[3 In the Pāli language Drist the word does not exist, and it would be something like subsitituída by Muni, which has the same meaning -except, of course, the fact that “he who sees” further points in this case the seeing process. Here was however used the term Pāli ditthi so as to maintain the link with the term semantic ditthi. The alternate translation is then: “So lets see who (or have the opportunity - avaṭṭhāna) of being in their true and natural.” Sarup-vatta itaritaraṃ | | 4 | | (Otherwise) at other times we become (equal) to this activity (of mind).
 Challenges
Challenges - vatta Panza kilesa akilesā ca ca | | 5 | | Activities (Mental) are five, some non-contaminating other contaminants: pamanes-vipariyesa-vikappa-
Nidda-sati | | 6 | | Experience (Evident-Measurement), ii) misperception (Illusion), iii) Intentional Thinking / Willing, iv) Sleep / Numbness, v) Memory Mndfulness. i) pamanes, experience or clear-measurement Paccakkh’ānumān’āgamā honte pamāṇāni | | 7 | | -
-
- What one sees and looks directly (paccakha), taking as a reference - it’s called experience.
-
-
-
-
- [7] Literally: “What comes through direct visualization and measurement is called the experience”
-
-
-
-
-
-
- ii) Vipariyesa, misperception or illusion
-
-
-
-
- Micca vipariyeso-Nanam atad-rūpa-patiṭṭhitaṃ | | 8 | |
-
-
- Illusion is the wrong understanding, based on something (lit. “one way”) that is not really.
-
-
-
-
-
-
- iii) Vikappa, Thought Intentional / Keen
-
-
-
-
- Saddam-ñāṇānupattī vatthu-Sunna vikappo | | 9 | |
-
-
- Intentional
Thinking / Willing is any way of understanding and unfounded assertion
(ie the internal speech, voltiva, partial and willful, based on mental
speculation). -
-
-
-
- [9]
Alternative translation: “Thinking is cognition without a sound object /
cause noise (vatthu).Think about it, thoughts are no more than sounds,
silent babble that passes through our being. -
-
-
-
-
-
- iv) Nidda, Sleep / Numbness
-
-
-
-
- abhava-paccay’-ārammaṇā vatta Nidda | | 10 | |
-
-
- Mental activity in the absence of mental objects is called Sleep / Torpor.
-
-
-
-
-
-
- v) Sati, the Memory / Mindfulness
-
-
-
-
- Anubhuti-visayāsammosā sati | | 11 | |
-
-
- Not to be confused (or not lose) the object (sensory) previously experienced is called Memory / Mindfulness.
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Abhyasa-virāgehi Tesam nirodho | | 12 | |
-
-
- The extinction of these [activities] comes from the practice of detachment / cessation of passions (turning)
-
-
-
-
- [12] We have here the words turn and nirodha in the same sentence! It can not be more Buddhist canon than this! Interestingly, however, is the current use and non-metaphysical terms of this stretch. They are applied in a simple process of meditation, in particular the process of concentration meditation. This can not go unnoticed and goes directly in line with readings jhanic cultivation practices in Buddhism.
-
-
-
 The Training
The Training 
-
-
-
- tatra-tiṭṭha yatano abhyasi | | 13 | |
-
-
- The
practice’s commitment to non-movement (ie, become mentally property (at
the same time it parmanece fluid - an excellent description for the
concentration!) -
-
-
-
-
-
- so-Kala-pana Dīgha nirantara-sakkār’āsevito dalhia-bhumi | | 14 | |
-
-
- Mast this (practice) must be based firmly in a long and careful exercise [excellent point here!]
-
-
-
-
- [14]
This goes in line with what the author wrote the medieval Pali
subcomentários the volume of the Digha Nikaya, where also we find the
combination of the terms and dalhia bhumi - “firmness” and
“establishment” - in the same sentence, denoting ” firm establishment “ -
-
-
-
-
-
- diṭṭhānusavika-visaya-vitaṇhāy
a Vasik-Sannes viraga | | 15 | | -
-
- Detachment is the mastery (VASI-kara) of perception, the dropping of the seat (vitaṇhā) by the following (anu-savika, lit.’s Subsequent flow) experience a prey to view.
-
-
-
-
-
-
- parama-tam Puris akkhātā guṇa-vitaṇhaṃ | | 16 | |
-
-
- This is the climax: the abandonment of the current headquarters of the senses, based on personal revelation / knowledge of self.
-
-
-
-
- [16] Here we turned a Brahman, is this approach that allows the soul to win the seat / attachment, Tanh. And this short sentence has much to offer! At
that moment in history, Patanjali was so convinced of the Buddhist goal
of “opening up the attachment, the seat stop,” which boils down to vitaṇhā term he uses. However,
it does not give up without a soul which its theistic philosophy simply
collapses and nothing in the text would make it distinguishable from a
treatise on the Buddha Dhamma. Thus,
mounted on a meditative Buddhist terminology and guidelines in the
conversation he introduces the term “Puris, which can be read as” soul,
“saying that the more you get closer to its” intrinsic nature “(svarūpa)
and inner body “Puri, or soul, you become able to stop itself this seat
/ attachment. Interesting. -
-
-
-
 Realization - Jhana / Dhyanas
Realization - Jhana / Dhyanas 
-
-
-
-
- The first jhana / Dhyāna
-
-
-
-
- vitakka-vicar-Anand-Asmita rūp’ānugamā sampajaññatā | | 17 | |
-
-
- This
is the alertness (sampajañña) from (the) (Kingdom of) form: a
self-directed thought-based consciousness, which remains (to this) and
inner happiness. -
-
-
-
- [17] Here we describe an almost identical description of the first jhana used time and again by the Buddha in Pali texts ( see this example ). Indeed,
we have a very beautiful description of the first jhana as a form of
sampajaññatā (fully aware of what is happening), after the plan of the
form (the theme of our meditation is a mental form) and a combined
happiness at the thought we are trying to grasp what itself could be
described as the pure experience of “I am” (Asmita - the term is being
used more loosely in place as would suttas). -
-
- However,
the announcement vitakka / vicara the first mention of meditative
absorption is a clear reference to the origin of Buddhist Yoga Sutra. Interesting also is the connection that is being done now with sampajaññatā: Think of everything we have said before about sati. If sati is simply the seizure of an object (the paṭṭhāna
of sati, so to speak), so it’s interesting to see how sampajaññā this
case, is identified with the state of the first jhana. Could this mean that when the Buddha mentions these two texts in Pali, which implicitly means samatha-vipassana?
-
- This
is not at all a strange idea, like many vipassana meditators, focusing
on objects will be much more subtle quickly show signs of the first
jhana. Could it be then that the term “sampajaññatā” was seen as the first result of a concentrated mind? -
-
- In
any case, experience will teach you very quickly that when you try to
hold an object in your mind, your awareness of what happens at this time
will increase dramatically, simply due to the fact that his effort to
keep the object is under constant danger during the siege of sense. -
-
-
-
-
-
- saw-Paticca Abhyasa-anno-pubbo saṃkhāraseso | | 18 | |
-
-
- (This accomplishment) is based on detachment and previously applied for any subsequent activities.
-
-
-
-
-
-
- bhava-Paticca videha-prakriti-layana | | 19 | |
-
-
- (For example) Based on this existence and the characteristics of self
-
-
-
-
-
-
- saddha-viriya-sati-samadhi-
paññā-pubbaka itaresam | | 20 | | -
-
- This
flower gives himself (based on these qualities) of conviction (saddha),
energy (viriya), mindfulness (sati), concentration (samadhi) and wisdom
(paññā) -
-
-
-
- [20] The Buddha mentions these five factors when he was training arupa jhana under his previous two teachers. He also mentions how crucial factors when striving for enlightenment under the Bodhi tree. Later,
during his years of teaching, he gave the name of “powers” (bullet) and
explained that, if perfected, would lead to enlightenment.
-
-
-
-
-
- Tibba-saṃvegānām āsanno | | 21 | |
-
-
- (For those) with a firm determination reached (this accomplishment, the first Dhyana / jhana).
-
-
-
-
-
-
 Advancing in jhana, tips and tricks.
Advancing in jhana, tips and tricks. 
-
-
-
-
- Mudu-majjhim’ādhi-mattatā tato’pi Visions | | 22 | |
-
-
- There is also a differentiation between (achievement) lower, middle and high
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Issar paṇidhānā-go | | 23 | |
-
-
- Or based on devotion (devotion) to a Lord (a master of meditation).
-
-
-
-
-
-
- kilesa-kamma-vipākāsayā aparāmissā Puris-visions’ Issar | | 24 | |
-
-
- The Lord (the Master) that is no longer influenced by the outcome kammic impurities and past desires.
-
-
-
-
- [24]
Besides the question whether the term “Issar” found here could be read
as merely referring to a master of meditation (which fits perfectly into
the discussion until verse 27, where it starts to not fit any more) is
likely discussion, including on-line translation of the Yoga Sutra by Geshe Michael Roach . The
principle can be interpreted so as to skeptics recalling the first
sutta MN seemed more logical to assume Issar was first used to designate
“the Lord” (ie your God). -
-
- But with a little more research found that the term Issar Theragatha us are used to designate the “master”. Interesting is also the word in Pali āsayih replaced simple wish / desire - “Asa.” But
“almost” sounds like “Asava” that would fit even better in the context
of kamma and vipaka Asava.But the idea is very specific (”that which
flows within you, taking it) and may or may not be what was meant in
this passage. -
-
-
-
-
-
- tatra-niratisayaṃ sabbaññatā bījaṃ | | 25 | |
-
-
- It is this that lies the seed of omniscience unmatched.
-
-
-
-
-
-
- sa pubbesam api guru kālen’ānavacchedanā | | 26 | |
-
-
- This Master from the beginning never abandoned him or abandon
-
-
-
-
- [26] Literally, “not” drop “(an + evaluation + chedana), or abandon, even for a time (short) (Kalena)
-
-
-
-
-
-
- tassa vācako Panavia | | 27 | |
-
-
- His Word is the breath and the clamor of living
-
-
-
-
- [27] On the panavah term, which can be interpreted as “om” in Hindu literature. It
all depends if we read verses 24-27 as involving “Issar” to mean “God”
or simply refer to consider meditation master of meditation you learn. If
you do a search in the Tipitaka, you see that when the Buddha used the
term was to refer to teachers (see for example Theragatha) -
-
-
-
-
-
- taj-tad-japp attha-bhavana | | 28 | |
-
-
- Praying in unison with this, this is the goal of meditation
-
-
-
-
-
-
- touch-pratyak cetanādhigamo’pi antarāyābhāvo ca | | 29 | |
-
-
- So if the mind itself and carries it away all obstacles / hazards:
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Vyadha-ṭṭhāna-samsaya-
pamādālayāvirati-bhrānti- dassanā’laddhabhūmikatvā’ navatthitatāni -
-
- Diseases,
skeptical questions, be moved to laziness of attachment, wrong view of
things, not meditative placements, or not yet firmly established in
these. -
-
-
-
-
-
- citta-vikkhepā te’ntarāyā | | 30 | |
-
-
- These are the causes of mental distractions (they fall due).
-
-
-
-
-
-
- dukkha-domanass’aṅgam ejayatv’assāsa-Passaseo vikkhepa-saha-Bhuvah | | 31 | |
-
-
- The physical and mental pain arises in the body, the shaking of the inhale and exhale conjução occur with such distractions.
-
-
-
-
- [31] Here dukkha and Domanassam mentioned. They also appear in the definition of the Buddha’s four jhana, but in a different direction. The problem described here meditative seems out of place and looks as if someone had to fit these words here. Also
the inhale and exhale clearly has an important role in that they cease
to exist (nirodha) so subjective to the practitioner in the fourth
jhana. It is strange that all this is on the list, but is presented in a very different interpretation.
-
-
-
-
-

 The Objects of Meditation
The Objects of Meditation
-
-
-
- tat-pratiṣedhārtham ekatattābhyāsaḥ | | 32 | |
-
-
- In order to control these distractions, this is the practice of unification of mind:
-
-
-
-
-
-
- metta-karuna-mudita Upekkha-sukha-dukkha-Visayan-
puññāpuñña bhāvanātassa cittapasādana ṃ | | 33 | | -
-
- The
cheerful calm the mind (citta-pasada) is achieved by meditation of
loving kindness, compassion, joy and equanimity in the face of pleasure,
pain as well as luck and misfortunes. -
-
-
-
- [33] And here we go. The
four brahmavihara, of course, famous for the way Buddha encouraged
monks to practice them to subdue the obstacles and enter the five jhana. It
is also interesting as the Tipitaka sometimes aligns them with the
progression in four jhana (which deserves to be studied separately). -
-
-
-
-
-
- pracchardana-vidhāraṇābhyāṃ go prāṇasya | | 34 | |
-
-
- Or the inhale and exhale, which is also an excellent exercise in meditation.
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Visayavati go pa-vatta uppannā manaso thiti-nibandhinī | | 35 | |
-
-
- It helps to stop and control the increasing mental activity that occurs through the power of the senses.
-
-
-
-
- [34
and 35] Wow, now includes Anapanasati to the list of meditation
techniques, the most favorite topics of Buddhist meditation, in addition
to brahmavihara, which “coincidentally” was mentioned in the previous
passage. Here
he almost “cites” the benefit of Anapanasati of Pali suttas, the Buddha
gave in the Anapanasatisamyutta Mahavagga, where it is clearly said
that the greatest benefit of Anapanasati is the ability to quiet the
mind. Very interesting!
-
-
-
-
-
- Visoko go jotimatī | | 36 | |
-
-
- And the mind becomes free from sorrow and radiant.
-
-
-
-
-
-
- vita-raga-visaya go citta | | 37 | |
-
-
- Free from desire for sense objects
-
-
-
-
- [36
and 37] These two passages seem more like a copy of what the Buddha
says in the suttas: “It is almost always remain in these states, O
monks, neither my body or my eyes get tired.” Although it immediately to
Explaining how the mind free from desires and radiant moves away from
the senses, as do the experienced meditators, this passage is important
because it shows that the author knew what he was talking in terms
pragmáticos.Não there is something more important to the induction of
samadhi (ie, jhana) that the resolution of the mind, the balance against
the attack of the senses to the mind. -
-
-
-
-
-
- svapna Nidda-go-jnānālambanaṃ | | 38 | |
-
-
- Of dreaming and sleep,
-
-
-
-
-
-
- yathābhimata dhyānād-go | | 39 | |
-
-
- parama-anu-stop-mahattvānto’
ssa vasīkāri | | 40 | | -
-
-
-
-
-
- kkhīṇa-vatta abhijātass’eva grahītṛ mani-Graham-grāhyeṣu stha-tat-tad-anjanatāsamāpatti | | 41 | |
-
-
- When
it happens in the destruction of mental activity or movement
[Khin-vatta], there is the appearance of a jewel, the emergence of
someone who carries such an object, the object and the carrying of such
an object in itself - and this immobility is what is called a
realization, or state of completion. -
-
-
-
-
-
- tatra-nana-saddattha vikappaiḥ saṃkiṇṇā savitakkā Samāpatti, | | 42 | |
-
-
- There is the state of realization is “with thought” and marked by impurity of speech of conscious thought, the internal speech.
-
-
-
-
- [42], in the Pali Canon parlance we would say “savitakka-jhana.”
-
-
-
-
-
-
- sati-parisuddhaṃ svarūpa-suññevattha-matta-
nibbhāsā nivitakkā | | 43 | | -
-
- (However)
there is a state of achievement without thinking (nirvitakka) with full
attention and clearer that it is the nature of emptiness without a
voice. -
-
-
-
- [43] parisuddham sati is obviously the name the Buddha gave to the fourth jhana. It
seems that the author tries to show us the range of four jhana,
pointing to the criteria of the first, and then, in contrast to the
characteristics of the fourth jhana again using the terminology of the
Pali suttas. -
-
-
-
-
-
- etadeva savic Nirvicārā ca-sukkhuma visaya akkhātā | | 44 | |
-
-
- Likewise, the state with and without research and consideration (vicara) is judged by subtlety of the object.
-
-
-
-
- [44] Here we are somewhat hampered by the language, and tempted to ask: by whom discerned before the non-self (anatta)?
-
-
-
-
-
-
- sukkhuma-visayattaṃ c’āliṅga-pary’avasānam | | 45 | |
-
-
- It culminates in a subtle object with no features
-
-
-
-
-
-
- tā eva sa-Bijo samādhi | | 46 | |
-
-
- But even this is a samadhi with seed / question.
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Nirvicārā-visārad’ajjhatta-
pasado | | 47 | | -
-
- Happiness
is attained with the inner conviction without regard to the
concentration already (vicara, which is paired with vitakka) -
-
-
-
-
-
- itaṃbharā paññā tatra | | 48 | |
-
-
- In this way, the truth is filled with wisdom.
-
-
-
-
-
-
- sut’ānumāna paññāyā-anna-visaya vises’atthatā | | 49 | |
-
-
- And this wisdom is of a different kind of knowledge acquired through learning.
-
-
-
-
-
-
- taj-jo-saṃkhāro’ñña Samkhara-paṭibaddhī | | 50 | |
-
-
- Such activity (meditative and induced) obstructs born (all) other activities.
-
-
-
-
-
-
- tassāpi nirodha Sabba-nirodha nibbījo samādhi | | 51 | |
-
-
- With the extinction of it all is also stopped - and this is the root-without-samadhi (samadhi-unborn)
-
-
-
-
- [51]
This last sentence sounds more like a reporter who, after being invited
to a very important meeting, is eager to share what he heard from
relevant sources. -
-
- Here
we are given a definition, in fact, the definition of the Buddha
“phalasamāpatti” - a state of jhana, which can only happen after someone
has had a realization that the particular insight nirvanic, giving you
access to that which is samadhi no “seeds” (nibbīja). -
-
- This
whole concept fits nicely into a row of theistic argument, and no
attempt is being made here in the final set of samadhi, to explain it. -
-
- Did
the Buddhists speak of this matter so that among the philosophical
circles “mainstream” of the time it was automatically understood as “the
highest you can get,” and the argument was so powerful that, despite
not fit in the school already thinking of the times (an ancient
Hinduism) was considered indisputable? -
-
- Hard to say. This
argument appears in the Sutta Ratanasutta Nipata.Vemos this final
state, without seeds, as something that would target when trying to
“Sanna-vedayita-nirodha” cessation of perception and feeling, a
realization of the Buddha described as possible Arahants Anagami for
that, after entering the eighth jhana sequentially finally leave the
activity more subtle (the sankhara) back.
-
-
-
-
-
- Patanjali Yoga viracite-iti-samadhi sutta paṭhamo-pated | | |
-
-
- This is the first chapter on the Samadhi Yoga Sutra of Patanjali.

…
- Source for adaptation and translation http://theravadin.
wordpress.com/2010/08/28/the- yoga-sutra-a-handbook-on- buddhist-meditation/ -
-
- Published with Blogger-droid v1.6.5
-
-
- Posted by Dhammarakkhittas at 15:31
-
-
- Labels: ashtanga yoga , Brahmanism , Buddha , B
uddhism , ancient Buddhism , dharma , dhyana ,Hinduism , jhana , patanjali , Sangha , Theravada , yoga , Yogasutra -
-
-
Reactions:
-
-
-
0 comments:
-
-
-
Post a comment
-
-
-
-
- http://yoga.org.nz/postures.
htm -
-
Main Page
Welcome to our yoga postures section. Here you will find
yoga moves that are broken down to the bare basics with colour photos
to match. We also have state of the art flash yoga animation technology that you can use to view these moves in full screen size, full colour and with full instruction.
Yogic exercises cater to the needs of each individual
according to his or her specific needs and physical condition. They
involve vertical, horizontal, and cyclical movements, which provide
energy to the system by directing the blood supply to the areas of the
body which need it most.
In yoga, each cell is observed, attended to, and
provided with a fresh supply of blood, allowing it to function smoothly.
The mind is naturally active and dynamic, while the innerself is
luminous. In this section we will give you plenty of yoga images and
instruction.
|
Breathing Pose
|
Arm Stretch
|
Kneeing Twist
|
||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
||||
Yoga breathing is also call Pranayama . Many say that Pranayama (Rhythmic control of breath) is one of the bests medicines in the world . Right click the link and save as to download a beginners breathing routine . Then watch in windows media player. Click the BIG play button in the middle below. To watch a Pranayama Breathing overview . Please visit: http://www.youtube.com/watch?
|
Hero Pose
The purpose of this pose is to help give the entire
body a very complete stretch from the heels to the head. It improves
strength and endurance and helps to control your breathing in
conjunction with the movements of the body.
It eases and stimulates the joints especially the
knees, ankles and shoulders. It reduces and alleviates backache and
improves the circulation of the entire body.
 |
|
Instruction Table
|
|
|
1
|
|
| Come in to a position on your hands and your |
| knees with your knees together and your feet slightly wider than hip width apart. Your big |
| toes & little toes pressing firmly into the floor | |
|
2
|
|
| Push back with your hands & sit between your buttocks on the floor, make sure you roll your calf muscles out wards so your not sitting on them. |
|
|
3
|
|
 |
Make sure the inner calves are touching the outer thighs and your ankles are outside your buttocks, arms resting at the sides. |
|
4
|
|
 |
Inhale as you slowly raise your arms to shoulder height, shoulders down. |
|
5
|
|
 |
Exhale lengthen out through the fingertips & turn your palms to the roof. Inhale stretch your arms overhead. |
|
6
|
|
 |
Interlock the fingers. Slowly exhaling turn the palms towards the ceiling, and with a powerful push lift up from the belly into your chest and shoulders. |
|
7
|
|
 |
Exhale bring your hands down in a smooth continuance motion…. |
|
8
|
|
 |
Now bringing your arms interlocking behind your back with straight arms, being careful not to roll the shoulders forward, squeezing the shoulder blades together and opening the chest on the front of the body. |
|
9
|
|
 |
Inhale hands back to the side |
| Repeat 2-3 more times |
Please Visit:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?

Kneeing Twist Pose
Regular practice of the kneeling twist pose
will aid in your ability to rotate the spine and upper torso more
effectively, while increasing the flexibility and strength in your back
and abdominal muscles. It also massages, stimulates and rejuvenates the
internal abdominal organs.
This pose is a good beginners pose and will get you ready for more advanced twists.
|
To view in flash - click the image below
|
|
|
|
Instruction Table
|
|
|
1
|
|
 |
Sit on your heals with your knees together, the tops of the feet Arms relaxed by the side keep your base firm by contracting your buttocks. |
|
2
|
|
 |
Inhale, extending the spine upwards, exhale twist around to the Take a few breaths here, keeping the stomach soft and the eyes soft. Repeat on the other side |
Please Visit:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?

The Triangle Pose
Triangle pose tones the leg muscles, spinal nerves and abdominal organs; it contributes towards a strong healthy lower back.
The triangle gives an excellent and complete stretch
throughout the entire body.
|
To view in flash - click the image below
|
 |
|
Instruction Table
|
|
|
1
|
|
 |
Align yourself in mountain pose. |
| Continuing with your smooth |
| flowing breath | |
|
2
|
|
 |
Inhale deeply and jump your feet out landing approx 1.2-1.5m apart. your feet need to be in line and pointing forward at right angles. Next raise your arms to shoulder level, be sure that they are in line with each other. Stretch your arms out from the middle of your back. Lift your chest and look straight ahead. |
|
3
|
|
 |
Now turn your right foot out while keeping your hips to the front, and turn your left foot in from 90 to 70 degrees, by pivoting on your heel. Insure your right heel is in line with the instep of the left foot. |
| This is important as it sets the base for this pose. | |
|
4
|
|
 |
The kneecaps and thighs are pulling up, simultaneously pushing downward through your feet into the floor. Inhale, extend the spine, exhale as you bend to the right, pushing out from the hips, through the right arm… |
|
5
|
|
 |
Taking your right hand to a comfortable position on your leg, your left arm coming up to straight, moving down as far as possible without turning the hips or torso. Keep the thighs firm and rolling around towards the buttocks, moving the left hip back and open the chest. |
|
6
|
|
 |
Inhale, extend the neck and spine, exhale, turn your head to look up at your left hand. |
| Keep your head, your buttocks and your heels in one straight line,not looking down with you body, keep opening your whole body up. |
| Breathe easy. |
Click here to view the Triangle pose
http://www.youtube.com/watch?

The Tree Pose
This pose harnesses the powers of mental concentration, while
allowing you to calm the mind. It develops balance and stability, and
strengthens the legs and feet, also increasing flexibility in the hips
and knees.
The tree pose is a balance pose incorporating three lines of
energy, emitting from the centre outwards. One line proceeds down the
straight leg, one line extends up the spine and out the fingertips, and
the third moves outward through the bent knee.
|
To view in flash - click the image below
|
 |
|
Instruction Table
|
|
|
1
|
|
 |
Align yourself in mountain pose. |
| Continuing with your smooth |
| flowing breath | |
|
2
|
|
 |
On your next inhale; shift the bulk of your weight onto your left foot. Exhale bend the right knee, and assisting with your hand, place the sole of your right foot as high as possible into the left inner thigh, with toes pointing down, steady yourself, and |
| breathe easy. | |
|
3
|
|
 |
Next raise your arms to shoulder level, be sure that they are in line with each other. Stretch your arms out from the middle of your back. Lift your chest and look straight ahead. Keep completely focused on the pose. |
|
4
|
|
 |
Now bring your palms together in prayer position. Keeping your eyes focused on a point in front of you, will assist your balance. |
|
5
|
|
 |
Inhale as you raise your arms overhead keeping your palms together and stretching upwards through the fingertips. |
| Keep working your right knee back and contracting your buttocks muscles in and down. |
| Feel your abdomen plane and hips facing straight ahead, while lifting out of the waist. |
http://www.youtube.com/watch?
Virabhadra
The Warrior pose is
named after the mythic warrior-sage, Virabhadra. This challenging pose
strengthens the entire body while improving mental capacity and self
control.
It builds, shapes and tones the entire lower body. It tones the
abdominal section and helps to prevent, reduce and eliminate back pain.
The entire upper body -front and back- is worked and doing this pose
increases the capacity of the respiratory system.
|
To view in flash - click the image below
|
 |
|
Instruction Table
|
|
|
1
|
|
 |
Stand in mountain pose continuing with your smooth flowing breath. |
|
2
|
|
 |
Jump your feet sides ways and sweep your arms out to the side so your |
|
Visualise |
|
|
3
|
|
 |
Keep an awareness of this line as you turn your right foot out to 90 degrees and turn your left foot in to 70 degrees. Ensure the heel of your front foot aligns with arch of your back foot, hips facing forward. |
| If your body wants to turn off centre, counter-act it by pushing simultaneously in opposite directions from the centre line. | |
|
4
|
|
 |
Inhale, an as you exhale bend your right leg, pulling up with the outside and inside of the thigh to form a right angle at the knee. Only go as low as you can with out turning your hips off centre. |
| Ideally you want your knee directly above your ankle with you leg coming vertically out of the floor like pillar. Keep the power flowing through the back leg into the floor. |
|
|
5
|
|
 |
Inhale lift the spine; exhale turn your head to look over your right arm. Take a few deep breaths through the nose. Hold the pose and breathe smooth. Reverse the procedure back to mountain pose and repeat back to the other side. |
Please Visit:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?

Mountain Yoga Pose
The Mountain Pose is one of the most important poses in yoga. It is the start and finish point of all standing poses.
When standing in mountain pose, the mind is quiet,
and the body strong and still, like a mountain. This is a pose you can
practise in your daily life, practising to stand correctly will have a
profound influence on your physical and mental well being.
|
To view in flash - click the image below
|
|
|
|
Instruction Table
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
|
Stand with your feet hip width apart, so the outsides of the feet are almost parallel edged. Press and spread the toes into the floor. Feel the weight of your |
|
2
|
|
|
|
Lift the kneecaps up by contracting the front thigh muscles, but not locking the backs of the knees. Pull up with the back of the thighs, and activate the hip and buttocks to level the pelvis. |
|
3
|
|
|
|
Your hips should be directly over your knees, and your knees over your ankles. This gives you a stable foundation and by positioning the pelvis properly, keeps the spine healthy. |
|
4
|
|
|
|
Now extend the spine, by slowly inhaling, lifting up |
||
|
|||
|
|||
The Prayer Pose
This pose is simple, but very effective, and is a
key movement to more advanced poses. This pose will teach you how to
push from under the shoulders and out of the lats, the major muscle
group of the back. A key movement in a lot of yoga poses.
It strengthens and aligns the upper body while
releasing tension and increasing the circulation to the shoulder joint,
which is a ball and socket joint. It also aids in strengthening the
abdominal and lumber region as you look to form a solid base.
|
To view in flash - click the image below
|
 |
|
Instruction Table
|
|
|
1
|
|
 |
Centre yourself in mountain pose and take a few deep breaths here, breathing down into the abdomen, continuing the breathing that you are now familiar with. |
|
2
|
|
 |
Inhale, raise your arms to shoulder height and stretch them out in the opposite direction to each other |
|
3
|
|
 |
Now twist your arms from the shoulder and turning your palms upwards. Keep the body in a nice strong upright position |
|
4
|
|
 |
Bring your arms out in front of you, pushing your elbows firmly together and your fingers extending away from you, while focusing on pulling your shoulder blades together.. |
|
5
|
|
 |
Continue squeezing the elbows together as you bring your palms together |
|
6
|
|
 |
Now bend at the elbow and take the forearms to vertical. Keep pressing firmly with the palms and the elbows as you breathe the arms upwards. With each exhale moving slightly higher. |
movement will teach you how to push from under the shoulders and out of
the lats, the major muscle group of the back. A key movement in a lot of
yoga poses. This pose is simple, but very effective, and is a key
movement to more advanced poses.

The Shoulder Shrug
The shoulder rotation is another pose which can be practiced anywhere and at any time.
It strengthens and aligns the shoulder region while
releasing tension and increasing the circulation to the shoulder joint,
which is a ball and socket joint. It also aids in strengthening the
abdominal and lumber region as you look to form a solid base.
|
To view in flash - click the image below
|
|
|
|
Instruction Table
|
|
|
1
|
|
 |
Align yourself in mountain pose. |
| Continuing with your smooth |
| flowing breath | |
|
2
|
|
 |
As you inhale, lift your shoulders to your ear lobes, keeping the head erect and soft. |
|
3
|
|
 |
As you exhale, rotate the shoulders around |
| by pushing up out of the chest and squeezing the shoulder blades together, rotating them |
| in a full circle. | |
|
4
|
|
 |
Back down into mountain pose |
| Repeat 3 more times |
Please Visit:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?

The Lying Basic Twist
Doing this pose will rapidly increase strength and muscle tone in your midsection.
The lying twist is another pose which is very
simple yet extremely effective. This pose is soothing to the spine and
neck, and warms and frees the lower back and hips and it also improves
digestion and assists in toxin elimination.
|
To view in flash - click the image below
|
 |
|
Instruction Table
|
|
|
1
|
|
 |
Come to a position lying on your back and stretch your arms out to Move your shoulder blades under. Spread your toes apart. Feel the |
|
2
|
|
 |
Bend your knees as far as they come towards the chest.
|
|
3
|
|
 |
Inhale, keeping your knees and ankles together,
Exhale, rolling your knees to the right. Focus on keeping your arms pressing out wards and your shoulders pushing firmly into the ground. You may feel or hear your spine lengthening as it extends into the correct alignment. |
|
Knees & ankles together breathe, focus on creating length between the left lower rib and the hip,
|
|
|
4
|
|
 |
Now turn your head to look over your left hand. Relax in to this pose, stomach soft, breathing soft and relaxed. Reverse the pose back up and repeat to the other side |
Adhomukha Svanasana
The downward yoga pose is
named as such as it resembles the shape of a Dog stretching itself out.
This pose helps to strengthen, stretch and reduce stiffness in the legs
while strengthening and shaping the upper body. Dog pose Yoga Posture .
One of the main yoga asanas. If you have time for only one posture try
this one.
Holding this pose for a minute or longer will
stimulate and restore energy levels if you are tired. Regular practice
of this pose rejuvenates the entire body and gently stimulates your
nervous system.
|
To view in flash - click the image below
|
 |
|
Instruction Table
|
|
| 1 | |
 |
Come up onto your hands and knees with your knees hip width apart and the hands shoulder width apart, your fingers wide pressing firmly into the floor. |
| 2 | |
 |
Inhale, arch your spine and look up as you turn your toes under. |
| 3 | |
 |
As you exhale straighten your legs and pause here for a moment. |
| 4 | |
 |
Now push the floor away from you hands, positioning your body like an inverted V, achieving a straight line from your hands to your shoulders to the hips. Straight arms and straight legs. |
| As you inhale press downward into your hands and lift outward out of the shoulders. |
| Lift your head and torso back through the line of your body. |
Please Visit:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?
Paschimottanasana
The purpose of this pose is to give the entire back
of your body a very complete stretch from the heels to the head. It is
excellent for posture improvement and stimulates the internal organs as
well.
It adds in improved mental concentration and
endurance and helps to control and calm the mind. It relieves
compression while increasing the elasticity of the spine, it also
strengthens and stretches the hamstrings.
|
To view in flash - click the image below
|
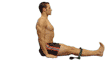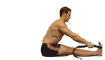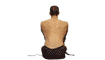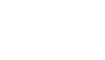 |
|
Instruction Table
|
|
| 1 | |
 |
Come to a sitting position with your legs together in front of you. |
| Move the fleshy part of your buttocks from underneath you, so you are on the top of your sitting bones, which are located at the very top of your legs. |
|
| 2 | |
 |
Roll the thighs inwards so that the kneecaps are facing directly upwards. |
| Activate the legs by pressing down into the floor, and out through the heels. |
| Spread your toes wide and pull them towards you. |
| Lengthen your lower back muscles down as you extend your spine up and out of the pelvis. | |
| 3 | |
 |
Now take your strap around both feet. The strap`s purpose is to keep the spine straight. This is very important. Be aware the head is an extension of the spine, so keep it aligned accordingly. |
| Use the breath to create the optimum degree of intensity in the stretch. | |
| 4 | |
 |
On your next exhale; come down the belt further while maintaining the extension on the front and back of the torso. Some of you will be able to grab the sides of your feet. Breathe softly and continuously. Don’t pull yourself forward by the strength of your upper body. |
| Keep bending at the hips, maintaining a relaxed head and neck. | |
| 5 | |
 |
Go a little further, relax your abdomen, and inhale, as you lengthen, exhale, and come further forward, increasing the space in your vertebrae. |
Please Visit:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?
Salabhasana
The locus yoga posture is
named as such as it resembles the shape of the insect known as the
Locust. This pose helps to strengthen, stretch and reduce stiffness in
the lower back while bringing flexibility to the upper back region.
When you first begin to practice this pose, your
legs may not move very far off the floor. Please continue and stay
positive as you will find your range will continue to improve the more
you practice. Learning to master this pose will hold you in good stead
for more advanced back bends.
|
To view in flash - click the image below
|
 |
|
Instruction Table
|
|
| 1 | |
 |
Come to a position lying face down on the floor, with your arms along side your body, palms and forehead down. Bring your knees and ankles together. Squeeze the shoulder blades together and down. Push your palms into the floor. Pull the abdominals inwards, contract the buttocks, and press the hips and pubis firmly into the floor. |
| 2 | |
 |
On your next exhale; raise the legs to a height that is comfortable but challenging. Keep the buttocks activated, lock the knees, keep the ankles together. |
| 3 | |
 |
Extend the front of your body as you pull the shoulder blades together, raising the head, the arms, and upper torso away from the floor, looking straight ahead, opening the front of the chest and pushing down the lines of the arms. |
| Keep the legs working strongly. |
Please Visit:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?

The Bridge Pose
The Bridge Pose is
a simple yet very effective pose to practice. It helps to promote a
healthy flexible spine while strengthening the legs and buttock muscles.
It also helps to stretch and stimulate the abdominal muscles and
organs.
It aids in easing and stimulating the mind and is a great way to reenergize if feeling tired.
|
To view in flash - click the image below
|
 |
|
Instruction Table
|
|
|
1
|
|
 |
Lie on your back with your legs bent, heels close to the buttocks, Feet pressing firmly into the floor, hip width and parallel. |
| Your arms should be slightly out from your sides, the palms of your hands pressing firmly into the floor. | |
|
2
|
|
 |
Inhale, and with the exhale raise the hips up by pushing strongly |
|
Take a few nourishing breaths in this position, as you keep opening the chest and lengthening the torso. |
|
|
3
|
|
 |
Now bring your arms over your head to the floor behind
you. Keep lifting your buttocks away from the floor, keeping them contracted, which will protect the lower spine, and work softly with the breath, keeping the head and neck relaxed. |
|
This
pose stretches the whole front of the body, and brings mobility to the spine. Breathing is improved from the opening of the ribcage and chest area. |

The Extended Child’s Pose / Garbhasana
The Childs Yoga pose when
practiced regularly is very beneficial to your entire mind and body. It
helps to release the pressure on the spine while providing an entire
stretch through the upper body to the fingertips. It also aids in
strengthening and stretching the insides of the legs while massaging the
internal organs.
Breathing will becomes more efficient and your mind
will become clear. It also aids in improved mental processes and helps
to rejuvenate and energize the entire being.
|
To view in flash - click the image below
|
 |
|
Instruction Table
|
|
|
1
|
|
 |
Bring your big toes together and your knees wide apart, inhale as you lift your spine and extend your stomach. |
|
2
|
|
 |
Exhale bend forward from the hips as you walk you hands out as far in front of you as possible, extending from the hips to the fingertips. |
|
3
|
|
 |
Place your forehead on the ground & buttocks
back to the heels. Work your pubis to the floor and strech the inner thigh muscles. Focus on the breath. |
|
4
|
|
 |
Breathing into the abdomen as you extend it forward in to the breastbone, creating length through the upper body. Exhale from deep in the abdomen relaxing in the spine and continue the slow controlled breathing. |
Please Visit:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?

The Standing Forward Bend
This pose aids in digestion and is restorative. It
frees the rib cage allowing for improved breathing. It aids in mental
concentration and helps to revive mental and pysichal exhaustion. The
heartbeat is slowed and the lower back is strengthened and pressure is
removed from the lumbar region.
It increases flexibility while strengthening and
developing the hamstrings. It also helps to strengthen the feet and
ankles while realigning the entire body.
|
To view in flash - click the image below
|
 |
|
Instruction Table
|
|
|
1
|
|
 |
Stand in mountain pose, in the centre of your mat, with your hands in prayer position. Jump your feet wide apart. Keep the outside of your feet running parallel while lifting your |
|
2
|
|
 |
Place your hands on your hips and feel the extension up out of the waist. |
|
3
|
|
 |
Inhale, As you exhale bend at the hips extend forward,
continue lifting out of the hips keeping your legs strong and your base nice and firm, looking forward to begin with. Keep the extension on the stomach, which will help keep your back flat protecting it. |
|
Take a few breaths here.
|
|
|
4
|
|
 |
Now take your hands to the floor extending from the lower abdomen to |
|
If |
|
|
5
|
|
 |
Draw your shoulders down your back so you can extend the neck with ease. |
| Remember to keep the arches high. |

The Boat Pose
Doing the boat pose will rapidly increase strength and muscle tone in your midsection.
Keep challenging yourself to stay in this pose
longer. If you find the stimulation of the midsection becoming intense,
just persist with it, knowing your mind has ultimate control over the
body.
|
To view in flash - click the image below
|
 |
|
Instruction Table
|
|
|
1
|
|
 |
Find yourself on your sitting bones, lifting out of the hips. |
| Extend your spine upwards, and press the soles of your feet into the floor, with the knees and ankles together. | |
|
2
|
|
 |
Using your fingertips on the floor for balance, extend your abdomen as you lean back slightly. |
|
3
|
|
 |
Bring your lower legs up, parallel to the floor.
Breathe softly, in and out through the nose, while opening the chest and squeezing the shoulder blades together. |
|
Focus on a point at eye level in front of you. You may find this pose challenging to begin with
|
|
|
4
|
|
 |
Now bring your arms up beside your knees, parallel to the floor, Feel the stimulation of the entire abdominal region, as you hold this pose for a few more breaths. |
|
Advanced Variation of The Boat
|
|
 |
Now bring your legs up to straight. Continue to keep your focus on that point in front of you. Continue with the controlled breathing. |
Posted by: site admin @ 8:01 am
swimming fitness
swimming fitness
schwimmen-0011.gif from 123gifs.eu Download
swimming
IN BRIEF: Moving through water by the motion of hands and feet.
I
often think that we are like the carp swimming contentedly in that
pond. — Michio Kaku, Source: Hyperspace : A Scientific Odyssey Through
Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th Dimension,
The Dream Encyclopedia:
Bodies of water are natural symbols of both the unconscious and the emotions. Dreaming about
swimming
can thus be related to the emotions or to an exploration of one’s
unconscious (a natural dream image for someone undergoing therapy).
Also, because we spend the first nine months of our lives in a liquid
environment, swimming is also a symbol of birth or rebirth.
Swimming
Swimming
and Diving - swimming: racing contest in which swimmers propel
themselves across surface of water over designated distance, usualy. in
one of four strokes
Swimming may refer to:
Movement and sport in water
Aquatic locomotion, animal movement through water
Human swimming, human movement through water
Swimming (sport), the competitive sport of swimming
http://www.active.com/swimming/Articles/Breathing-Tips-for-Swimmers.htm
When
it comes to breathing, new swimmers often struggle to master their
technique, while veteran swimmers continually strive to perfect it. Use
this guide to getthe air you need in the water.
Proper Breathing Technique for Swimming
Learn how to get comfortable in the water and find a rhythm to your breathing, even through a stressful triathlon swim start.
Bilateral Breathing
Many
swimmers use only one side to breathe on, especially those who log a
lot of freestyle yards. One of the most common questions in the swimming
world is should you breathe on one side only or use bilateral
breathing?
4 Steps to Easy Breathing in Freestyle
For beginning swimmers, learning to breathe is as important as
discovering your stroke. Here are four ways to gradually build your confidence
in the water.Breathing Mechanics That Will Help
Your Freestyle
If breathing breaks your stroke’s rhythm, the solution isn’t to
hold your breath. Use these tips to put air in your lungs without compromising
your technique.
Extra Air and Fast Turns in Distance
Swimming
Long pool sets mean lots of flip turns. For some swimmers, not
breathing in and out of the turn can leave them gasping for air. Next time
you’re short of breath, try this method.
Mastering the Top 5 Freestyle
Breathing Challenges
The most common questions I hear about the mysteries of swimming
efficiently usually involve breathing. Here are the top five challenges in
learning how to breathe in freestyle.
Breathing Basics: Getting Comfortable
Until your swimming breath becomes routine, effectively focusing
on other aspects of your stroke is impossible. Try this unique out-of-the-pool
exercise to help you get comfortable.
Inside-Out Breathing: Get the Air You
Need
There’s probably a greater range of breathing skill in swimming
than in any other activity. Elite swimmers can breathe effortlessly while
maintaining perfect form at maximum exertion and world-record pace.
Perfect Your Breathing With a Better
Body Position
Do you get fatigued easily in the water because of lack of air?
Improve your breathing by balancing your body position.
Q & A With Natalie Coughlin:
Breathing and Hand Position Tips
Olympic gold medalist Natalie Coughlin answers your questions on
maximizing your freestyle breathing and fine-tuning your hand position.
Q & A With Natalie Coughlin: Flip
Turns and Better Breathing
Olympian Natalie Coughlin answers questions about improving your
flip turns and having greater control over your breathing.
What is the definition for
swimming ?
In recreation and sports, the propulsion of the body through
water by combined arm and leg motions. Swimming is popular as an all-around
fitness routine and as a competitive sport. It has been included in the modern
Olympic Games since their inception in 1896. Events include freestyle
(crawl-stroke) races at distances of 50, 100, 200, 400, 800, and 1,500 m;
backstroke, breaststroke, and butterfly races at 100 and 200 m; individual
medley races at 200 and 400 m; freestyle relays, 4 ´ 100 m and 4 ´
200 m; and the medley relay, 4 ´
100 m. Long-distance swimming competitions, usually of 15 – 37 mi (24 – 59 km),
are generally held on lakes and inland waters.
Swimming is one of the most popular
recreational sports that can be enjoyed by all ages. The ability to swim
enables people to participate in a wide variety of water sports such as
snorkelling, water skiing, jet skiing, wind surfing, sailing, boating, fishing,
rowing, and canoeing, without the fear of getting into trouble, and reduces the
risk of drowning. Fear of water, particularly if a person suddenly gets out of
their depth, prevents a lot of people going into a swimming pool or enjoying
beach holidays. Many of the newer water sports require expertise in handling a
craft as well as swimming proficiency.
Water is a very dangerous place for non swimmers, particularly
if it is cold and an excessive amount of alcohol has been drunk. Unfamiliar
surroundings, and no knowledge of local tides, can be lethal to careless
individuals. Water-related fatalities are the second leading cause of
accidental death in the UK and Australia, and the third in the US. The risk of
drowning is 2.5 deaths per 100
000
in USA and 1 per 100 000
in the UK.
Babies are taught to swim at a very young age in some countries;
this enables them to learn to swim without fear of the water. They should have
had their first two combined immunizations, unless they are being breast-fed.
The water temperature should be higher than normal, a minimum of 86°F or 27°C.
The time spent in the water should be carefully monitored; this can vary from
10 minutes to 30 minutes but babies should not stay too long in the water as
they lose heat rapidly.
Swimmers are usually taught the four swimming strokes used for
competitions; the front crawl, backstroke, breaststroke and butterfly, which
are swum either as a single stroke or in combination over various distances.
There are four phases of each stroke; the reach, catch, pull,
and recovery. The arm action during the pull phase provides 75% of the
propulsion in all strokes except the breast-stroke, where the contributions
from the upper and lower limbs are equal. During reach or entry the arm reaches
forwards to enter the water. In backstroke the arm entry occurs with the
shoulder in the fully elevated position. Catch is similar in all competitive
strokes except backstroke; the elbow flexes, the arm extends forwards at the
shoulder and moves outwards in the horizontal plane whilst rotating towards the
body. The pull is the propulsion phase and can vary; the swimmer either sculls
or pushes the water. The arm action starts at maximum elevation and ends in
extension except in breast-stroke. Recovery is the out of water phase (except
breast-stroke), and the arm then returns to start position.
In breast-stroke the arms move together in pull and recovery
phase and the arms do not pull below the waistline.
Swimming is a sport that attracts participants of all ages
although it is largely a young sport. Competitions are organized by clubs,
schools, and national associations. Short course competitions take place in a
25-metre pool, long course in a 50-metre pool. Olympic swimming competitions
are over a variety of distances and strokes, and they take place in 50-metre
pools. Synchronized swimming, water polo, and diving are also included in the
Olympic program
. Swimming
in the sea may be part of a triathlon race, and open sea races, including
Channel swims, are also held. ‘Masters’ swimming competitions are held for
those over 24 years of age whereas ‘veteran’ sports competitions in athletics
are for the over 40s. Competitions for different age groups are held in most
countries, and world championships also take place.
Competitive swimming is a high-intensity training and
performance sport. During the school year swimming training is divided into two
sessions: the first session is in the early morning before school and the
second session after school. The competitive swimmer usually does an average of
12
000-18 000 metres per day. The competition programme
for the season should be planned well in advance so that the swimmer can peak
for a specific competition, i.e. the swimmer reduces the amount of training to
get the best result.
Swimming is a relatively injury-free sport and was found to be
the safest of eleven sports surveyed by Weightman and Brown in 1975. It is
non-load-bearing and does not involve antigravity work, resulting in fewer
injuries. The injuries that do occur are usually due to overuse, doing too much
too quickly, or breaking the rules.
To ignore warning signs of strong currents, king waves or rip
tides may have lethal consequences. Diving into the shallow end of a pool or
into a wave or sea where rocks are submerged may result in severe injuries.
Pools should have the depth clearly marked so that swimmers do not dive into
shallow water. Pools used for competition should be marked 2 metres from the
wall at each end to judge when to turn. Flags are placed above the pool 5
metres from the end of the pool for the backstroke turn. There are rules
against running around the pool. Pool discipline should be maintained,
particularly out of the pool to prevent people slipping or jumping into the
pool on top of other swimmers. There should also be strict discipline in the
pool when swimming lengths.
Hyperventilation before
trying to swim a long distance under water should be forbidden, as it increases
the risk of hypoxia
(lack of oxygen), and may result in loss of consciousness and
death by drowning. The hyperventilation removes carbon dioxide and hence delays
the stimulus to breathe when breathholding.
Swimming programmes are helpful for both the mentally and the
physically handicapped as they weigh less in water, and this makes it easier
for them to move their muscles, enabling them to improve muscle tone and
co-ordination of movement. Pregnant women can swim during their pregnancy while
many other sports are not suitable. Swimming is also useful in rehabilitation
of injured athletes. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis can improve their
aerobic capacity by swimming in warm water. Asthmatics should be encouraged to
swim, as swimming is the sport that is least likely to precipitate an asthmatic
attack, and the fitter they are the fewer attacks they have; swimming improves
their breathing. Asthma is not a handicap in achieving excellence in sport as
shown by the number of Olympic gold medal swimmers who were asthmatics.
Water aerobics is becoming a popular method of keeping fit, with
less potential for injury than high impact aerobics. Running in the water is a
useful method for athletes to keep fit, if they are injured and unable to cope
with full weight-bearing on hard surfaces. Hydrotherapy is also an effective
rehabilitation after injury. Swimming is thus a sport that can be enjoyed by
many different groups.
Read more: http://www.answers.com/topic/swimming#ixzz1TqUeuPf1
Read more: http://www.answers.com/topic/swimming#ixzz1TqTTVV9g
Q: What is Avantouinti?
Avantouinti
is the Finnish word for “winter swimming”. It may sound to many like
masochism taken to ridiculous lengths, but it is becoming increasingly popular
in Finland where 10% of the population have tried it and there are more than
80,000 regular winter swimmers who tout the therapeutic benefits of winter
swimming. The
typical swimmer is not some grizzled macho-type, but a middle-aged woman with a
clerical job.
Q: What Happens When You
Jump Into Cold Water?
Sudden
immersion in ice cold water can result in an involuntary
gasp followed by 1 - 3 minutes of involuntary hyperventilation. Specific data are: 2.0 liter gasp in 82o
water and 3.0 liter gasp in 50o water (i.e. nearly your entire lung
volume), and in 50o water a 600 - 1,000 percent increase in
ventilation (air in and out) in the first minute. This hyperventilation results
in a profound lowering of blood carbon dioxide levels and a raising of blood pH
levels.
Q: Is Winter
Swimming Dangerous?
The strain placed on the heart are not likely to be a problem
for a healthy, fit person but may be dangerous for those with underlying heart
disease or hypertension.
Professor William R. Keating from the University of London
indicates that there is little health risk in cold-water swimming unless a
person starts suddenly at an old age.
Q: What is Cold Water
Shock
Rapid
cooling of the skin triggers various heart and breathing responses. The heart
rate can increase by 50% and blood pressure increase can increase to 175/93.
Although a substantial strain on the heart, these changes are not likely to be
a problem for a healthy, fit person but may be dangerous for those with
underlying heart disease or hypertension.
Q: Why is Cold Water
Swimming Becoming a Fitness Fad?
The number of people who swear by the therapeutic qualities of
outdoor winter swimming have increased dramatically of late. Clubs have sprung
up across the country for the reason that it the ideal form of gentle health
care. The benefits can be very great, it can stimulate mental processes,
produce hormones which make the body able to cope with physical stresses and
can increase the level of mental awareness and a feeling of well-being.
It can also release stress, remove aches and pains, increase vitality and keep
skin looking younger. Apparently the frost is a great preserver!
Many even treat their asthma or arthritis with cold water swimming.
Dhammarakkhita











